SHPHE received repeat order from customer in Australia
Recently, SHPHE received repeat order from custome...
More
A plate style heat exchanger is a compact and efficient device designed to transfer heat between two fluids without mixing them. It consists of multiple thin, corrugated metal plates stacked together, creating alternating channels for hot and cold fluids. These exchangers are widely used in industries such as chemical processing, HVAC, food and beverage, and power generation due to their superior thermal performance, scalability, and space-saving design. Compared to traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers, plate style models offer higher heat transfer coefficients, lower energy consumption, and easier maintenance. Their modular construction allows for customization to meet specific thermal requirements, making them a versatile choice for diverse applications.
Plate heat exchangers are constructed from materials like stainless steel, titanium, or nickel alloys to withstand corrosive environments and high temperatures. They can handle pressures up to 25 bar and temperatures ranging from -40°C to 200°C, depending on the model and gasket materials. Modern designs also feature brazed or welded plates for leak-proof operation in demanding conditions. With heat transfer efficiencies exceeding 90%, these systems significantly reduce operational costs and energy waste. Industries adopting plate heat exchangers report up to 50% savings in energy usage compared to conventional systems, according to case studies from manufacturers like Alfa Laval and SWEP.
The working principle of a plate style heat exchanger relies on conductive and convective heat transfer through its plate stack. Hot and cold fluids flow in alternating channels, separated by the thin metal plates. The corrugated plate design creates turbulent flow, enhancing heat transfer efficiency by disrupting boundary layers and maximizing surface area contact. Fluids typically enter through inlet ports, distribute via gasketed or welded channels, and exit through outlet ports, with counter-current flow arrangements optimizing temperature differentials.
Advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling shows that plate heat exchangers achieve thermal effectiveness ratings of 80–95%, far surpassing shell-and-tube designs. For example, in a dairy pasteurization system, a plate exchanger can heat milk from 4°C to 72°C in seconds while cooling the heating medium simultaneously. The gap between plates (1–5 mm) ensures minimal hold-up volume, critical for sanitary applications. Some units incorporate specialized plate patterns (e.g., herringbone or chevron) to handle viscous fluids or particulate-laden streams. Real-world performance data from HVAC installations demonstrate 30–40% faster heat recovery compared to tubular models, with compact units providing up to 3x more surface area per cubic meter.
Select the most popular foreign trade service products to meet your diverse needs
Learn more about the dynamics and professional knowledge of the foreign trade industry
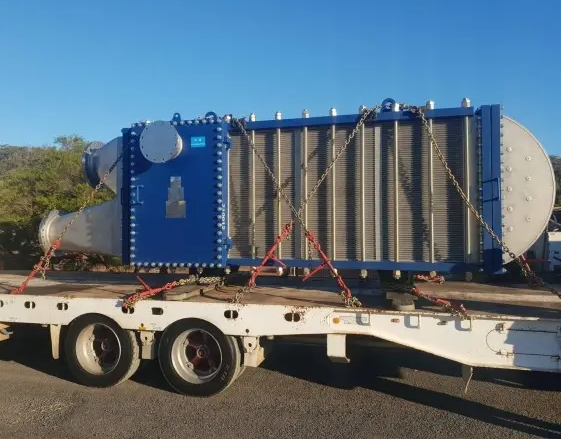

Recently, SHPHE received repeat order from custome...
More
Understanding welded heat exchanger's unique const...
More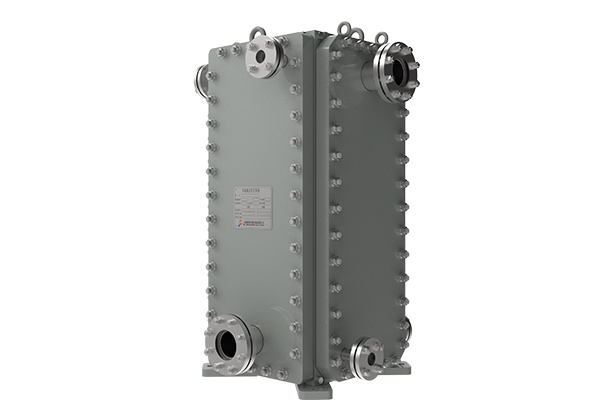
Traditional plate heat exchangers (PHEs) use gaske...
More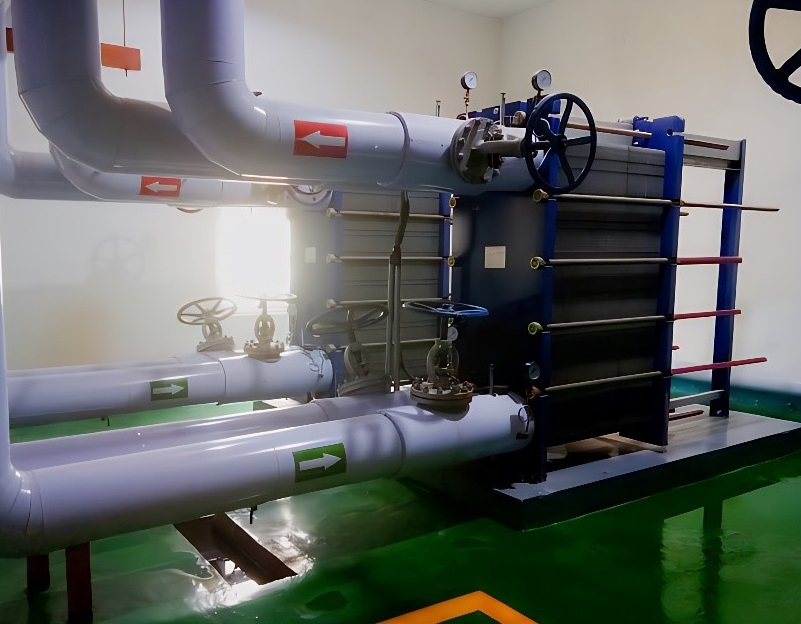
This guide offers a comprehensive examination of t...
More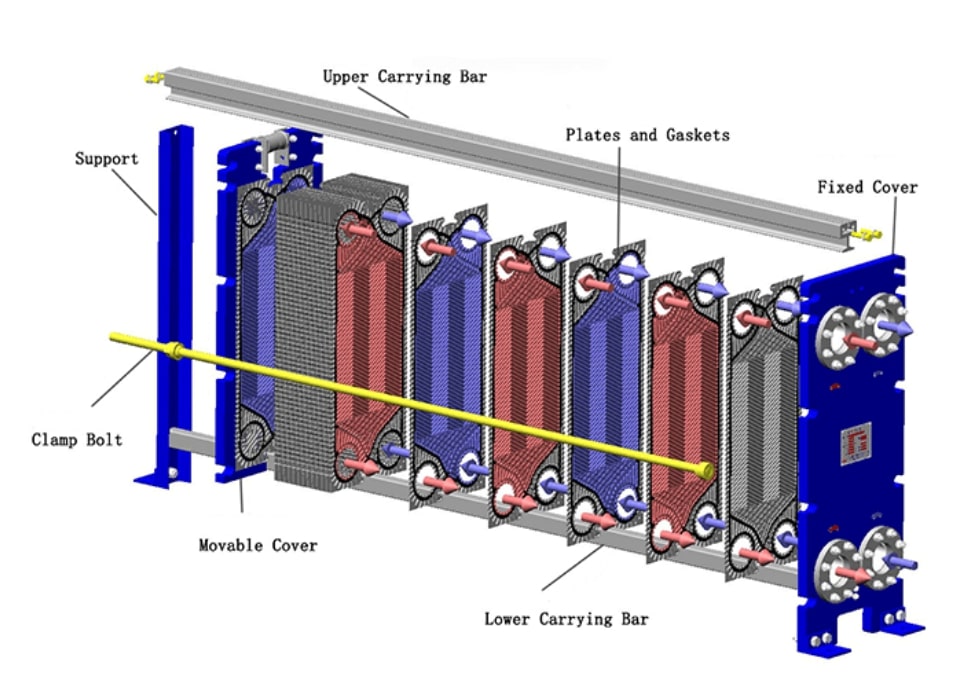
Plate heat exchangers (PHEs) are often the most ef...
More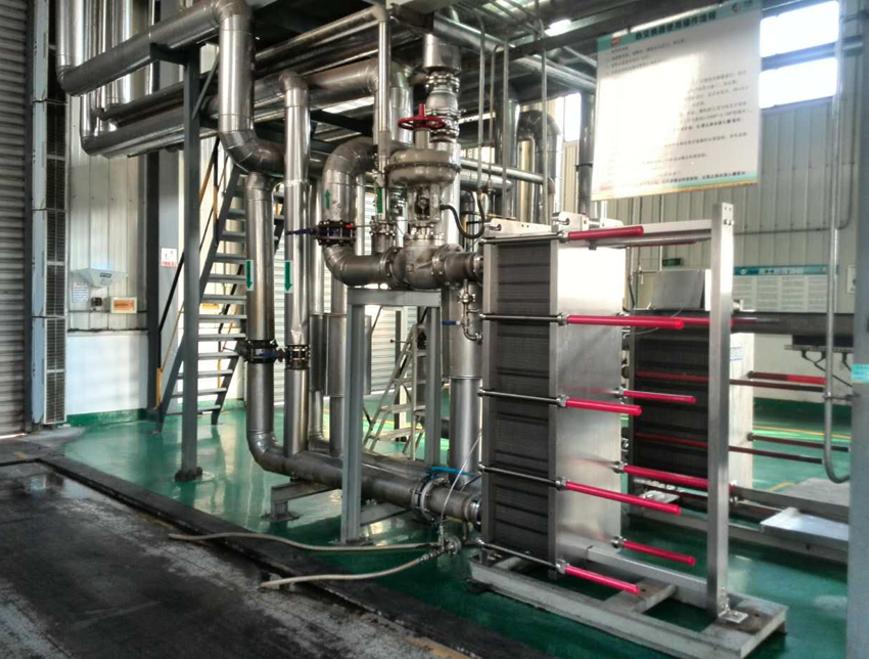
A plate heat exchanger (PHE) is a device engineere...
MoreExplore more content related to foreign trade services
