Comparing welded block and gasketed plate heat exchangers
Comparing welded block and gasketed plate heat exchangers
You can see clear differences between welded block heat exchangers and gasketed plate heat exchangers. Welded block heat exchangers are good for aggressive fluids. They can handle high pressure or high temperature. Gasketed plate heat exchangers are popular because they work well and can be used in many ways. You should pick a heat exchanger by thinking about what you need, how well it must work, and how much care you want to give it.
Welded Block Heat Exchanger vs Plate Heat Exchanger Design

Welded Block Heat Exchanger Structure
A welded block heat exchanger looks strong and small. Makers use laser welding to join metal plates. This creates tough channels for fluids to move through. The welded block heat exchanger can handle harsh fluids and high pressure. It does not need gaskets, so leaks are less likely. You also do not have to fix it often. The welded block heat exchanger uses metals like copper, aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, nickel alloys, and graphite. Each metal has special qualities. Copper moves heat well. Titanium and nickel alloys do not rust easily. The chart below shows how these materials compare:
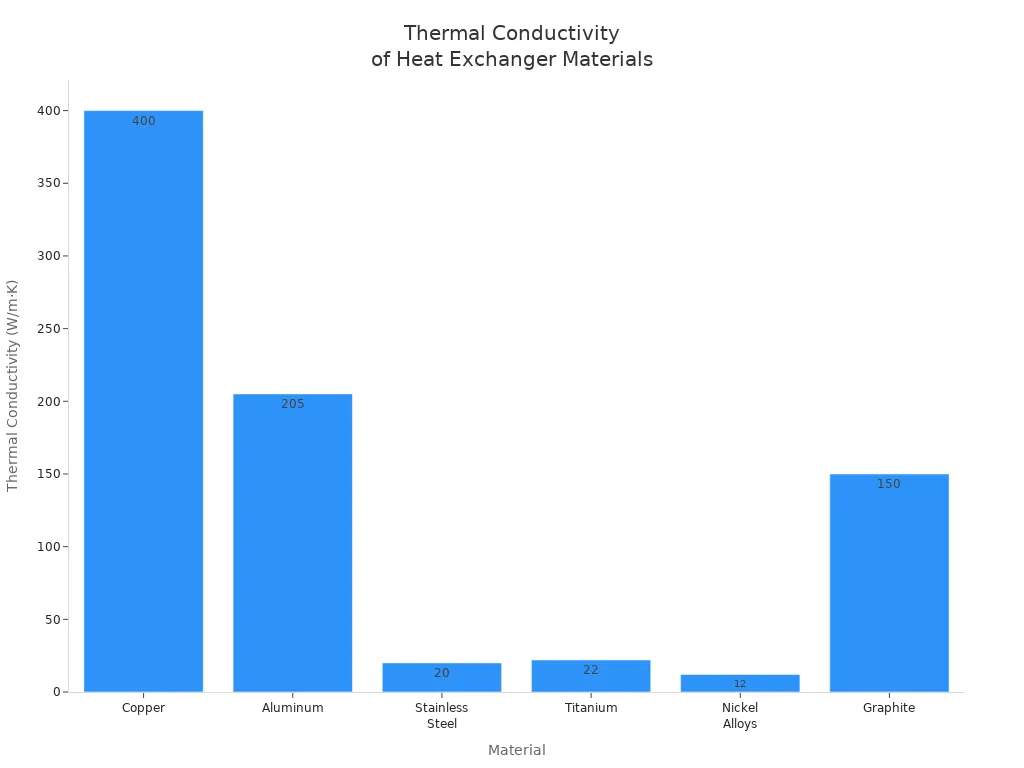
Tip: Pick a welded block heat exchanger if you need something tough for hard fluids or very strong conditions.
Plate Heat Exchanger Structure
A plate heat exchanger has thin plates with wavy shapes. Gaskets sit between each plate to seal the channels. This stops fluids from mixing. Pressure plates keep everything tight and safe. You can open the unit easily to clean or check it. This makes plate heat exchangers simple to take care of. You can separate the plates to clean them well. You can also change the unit for new jobs or look inside without trouble.
Here is a table that shows why plate heat exchangers are easy to care for:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Compact Design | Fits in small places and is easy to clean. |
Plate Separation | Plates come apart for cleaning and checking. |
Flexibility | Can be opened for service or changed for new needs. |
Hassle-free Inspection | Opens and closes quickly for fast checks. |
Adaptability | Can be changed for different uses. |
Key Design Differences
You can see how welded block heat exchangers and plate heat exchangers are different in the table below:
Aspect | Welded Block Heat Exchanger | Plate Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|
Construction | Metal plates joined by laser welding | Plates stacked with gaskets |
Materials | Copper, aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, nickel alloys, graphite | Stainless steel, titanium, other alloys |
Sealing Method | Welded channels, no gaskets | Gaskets between plates |
Maintenance | Needs little care, rarely fixed | Easy to clean, plates open up |
Pressure/Temperature | Handles high pressure and heat | Good for low or medium pressure |
Fluid Compatibility | Works with harsh fluids and tough places | Works with gentle fluids, flexible use |
Pick a welded block heat exchanger if you want something strong for rough fluids. If you want easy cleaning and more choices, a plate heat exchanger is better.
Performance and Efficiency in Heat Exchangers
Thermal Performance Comparison
You want your heat exchanger to move heat fast and save energy. Both welded block and plate heat exchangers move heat well. Welded block designs use pure countercurrent flow. This means hot and cold fluids go in opposite ways. This helps the fluids get very close in temperature, sometimes only 1°C (2°F) apart. Plate heat exchangers also move heat well. They work best with gentle fluids or when you need to change setups.
Here is a table that shows how each type works in different ways:
Feature | Welded Block Heat Exchangers | Plate Heat Exchangers |
|---|---|---|
Durability | Known for being tough and lasting in hard places | Known for working well and being reliable |
Temperature Fluctuation | Made to handle hard jobs with one or two phases | Works well with harsh fluids and coolants |
Cleaning Accessibility | Easy to clean with tools and check inside | Plates come apart for cleaning |
Thermal Performance | Pure countercurrent flow, very close temperatures | Almost the same heat transfer as gasketed plates |
Note: If you want strong heat transfer and close temperatures, welded block heat exchangers are a good choice.
Pressure and Temperature Capabilities
You need to know how much pressure and heat your system will have. Welded block heat exchangers can handle strong fluids and tough conditions. You can use them where pressure or temperature changes a lot. Plate heat exchangers work well for low or medium pressure and heat. They fit many jobs but may not last as long in hard places.
Here is a table that compares the highest ratings for each type:
Heat Exchanger Type | Max Temperature (°C) | Max Pressure (bar) |
|---|---|---|
Semi-welded GPHE | 180 | 16/20 |
Welded Block HE | Higher (depends on design and material) | Higher (depends on design and material) |
Welded block heat exchangers do not use gaskets. You do not have to worry about leaks from pressure or heat changes. You can trust them with strong fluids or when safety is very important.
Maintenance and Cleaning Needs
You want your heat exchanger to work well without fixing it all the time. Welded block heat exchangers need little care. You do not have to change gaskets or worry about leaks. You can clean them with tools and check them easily. Plate heat exchangers let you open them and take out the plates. You can clean each plate and look for damage.
Tip: If you want fewer leaks and less fixing, welded block heat exchangers are safer.
You should pick your heat exchanger based on what you need. If you want strong heat transfer, high efficiency, and little care, welded block heat exchangers are best for hard jobs. Plate heat exchangers are good for easy cleaning and flexible use.
Application Suitability for Heat Exchanger Types

Best Uses for Welded Block Heat Exchangers
Pick a welded block heat exchanger for hard jobs. It works well with strong fluids and high pressure. You use it where leaks cannot happen. Welded block heat exchangers are found in chemical plants and oil refineries. They are also used in power stations. Food and beverage factories use them for pasteurization and cooling. These heat exchangers keep fluids apart and safe. They work well even in tough places. You get good results and fewer leaks.
Best Uses for Plate Heat Exchangers
A plate heat exchanger is easy to clean and change. You can use it for many heat transfer jobs. It works best with gentle fluids. You can open it up to clean inside. Plate heat exchangers are used in food factories and HVAC systems. Dairy plants use them too. They help control temperature and stop contamination. You can change the setup if you need to. Here is a table that shows why plate heat exchangers are good for HVAC systems:
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Compact Design | Gives lots of heat transfer in a small space. |
Enhanced Efficiency | Wavy plates mix fluids and help heat move faster. |
Easy Maintenance | You can clean and fix it easily for good use. |
Modular Construction | You can add or change parts for your needs. |
Tip: Plate heat exchangers are good for easy cleaning and changing.
Industry Application Examples
Different heat exchangers are used in many places. Welded block heat exchangers help with pasteurization and cooling in food factories. They also make cold storage work better and save energy by up to 25%. Plate heat exchangers are used most in food processing. You use them for milk pasteurization and making dairy products. You can take them apart to clean, which helps keep things clean. Plate heat exchangers are also found in HVAC systems. They save space and make things work better. Both types help move heat in many industries.
Pros and Cons of Welded Block and Plate Heat Exchangers
Welded Block Heat Exchanger Pros and Cons
You can count on a welded block heat exchanger when you need strength and safety. This type of heat exchanger uses welded plates to create strong channels. You do not need gaskets, so you worry less about leaks. You get high heat transfer even with aggressive fluids. You can use welded block heat exchangers in places where shell and tube heat exchangers might fail. These units handle high pressure and temperature well. You do not have to clean them often, and you do not need to replace gaskets.
Here are the main pros and cons:
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Handles high pressure and temperature | Higher initial cost |
Works with aggressive fluids | Harder to expand or modify |
Low risk of leaks | Cleaning can be more complex |
Long service life | Not as flexible as plate heat exchangers |
Tip: Choose welded block heat exchangers for tough jobs where leaks are not an option.
Plate Heat Exchanger Pros and Cons
You get many benefits from plate heat exchangers. These units give you high heat transfer in a small space. You can open them up and clean them easily. You can change the number of plates to fit your needs. Plate heat exchangers cost less at the start than welded block heat exchangers or shell and tube heat exchangers. You save money if you have a cost-sensitive project. You also get high energy efficiency and lower maintenance costs.
However, you need to watch for some problems. Plate fouling can happen, which means you need to clean the plates often. Corrosion can cause leaks, so you must pick the right materials. The seals and gaskets are important. If they fail, you can get leaks and lose efficiency. Regular checks and good materials help prevent these issues. Gasketed plate heat exchangers need more care than welded plate heat exchangers or brazed plate heat exchangers.
Here is a quick list of common maintenance challenges:
Fouling
Corrosion
Seal and gasket failures
Operational problems
You can reduce these problems by:
Cleaning plates often.
Checking seals and gaskets.
Running the unit the right way.
Note: Plate heat exchangers work well for many jobs, but you need to keep up with cleaning and checks.
You can use plate heat exchangers in food, HVAC, and shell and tube heat exchangers replacements. You get flexibility and easy service, but you must manage maintenance.
You need to pick a heat exchanger that fits your job. Welded block units are best for high pressure and strong fluids. They also work well in tough places. Plate models are good for gentle fluids. They are easy to clean. The table below shows why welded block units are good for hard jobs:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Leak-proof operation | Welded units do not use gaskets. They work well with strong fluids and steam. |
Pressure and temperature limits | Welded block units handle up to 40 bar and 400 °C. They save space and work efficiently. |
Proven applications | Welded block units are used in power, chemical, food, metallurgy, and HVAC jobs. |
Here are some tips for choosing a heat exchanger:
Check what your system needs.
Make sure the fluid matches the right material.
Think about space, how to care for it, and safety.
FAQ
What is the main difference between welded block and plate heat exchangers?
Welded block units have welded plates and no gaskets. Plate heat exchangers have gaskets between each plate. Welded blocks are good for hard jobs. Plate models are simple to clean.
How do I choose the right heat exchanger for my system?
You need to look at your fluid type. Check the pressure and temperature you need. Pick a plate model if you want easy cleaning. Choose a welded block if you need strength for tough fluids.
Can I clean a welded block heat exchanger easily?
You clean it using special tools. You cannot open it like a plate model. Cleaning takes longer, but you do not change gaskets.
Are plate heat exchangers safe for aggressive fluids?
Plate heat exchangers work best with gentle fluids. Aggressive fluids can hurt gaskets and make leaks. Welded block designs are better for strong chemicals.
What industries use these heat exchangers?
Industry | Common Use |
|---|---|
Food & Beverage | Pasteurization |
Power Plants | Cooling |
Chemical Plants | Fluid separation |
HVAC | Temperature control |





