Plate to Plate Heat Exchanger Models Compared for Industrial Applications
Industrial leaders consistently select the Shanghai Heat Transfer Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger when seeking advanced performance and reliability. The market for plate to plate heat exchanger models reached USD 5.98 billion in 2024, with HVAC and refrigeration holding the largest segment. Key comparison criteria include efficiency, total cost of ownership, and environmental impact.
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Efficiency | Involves thermal performance, pressure drop, fouling resistance, and maintenance requirements. |
Total Cost of Ownership | Includes initial purchase price and long-term operational costs, highlighting the financial impact. |
Environmental Impact | Focuses on sustainability, material usage, and carbon footprint associated with manufacturing processes. |
Leading Plate to Plate Heat Exchanger Brands

Shanghai Heat Transfer Gasketted PHE
Shanghai Heat Transfer stands out in the heat exchangers market with its Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger. This model showcases advanced heat exchanger technologies that deliver high efficiency and operational flexibility. The compact, modular design allows for a high surface-area density, which supports energy savings and a reduced footprint. The use of premium materials such as stainless steel and titanium ensures durability in demanding industrial environments. The Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger features innovative plate patterns that create turbulent flow, maximizing heat transfer and minimizing energy loss. Maintenance remains simple due to the Clean-in-Place compatibility and low fouling design. These strengths make Shanghai Heat Transfer a preferred choice for industries seeking reliable and sustainable solutions.
Tip: For industries that require both performance and easy maintenance, Shanghai Heat Transfer’s Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger offers a leading solution.
Tranter, API, and Kelvion Overview
Several other brands also play a significant role in the heat exchangers market. Tranter provides a wide product range with advanced sealing technology and easy maintenance. API focuses on enhanced heat transfer surfaces and flexible design options, supported by strong engineering expertise. Kelvion offers optimized flow paths and anti-fouling designs, along with high-temperature resistance and customized solutions. These companies contribute to the advancement of advanced heat exchanger technologies, ensuring that industrial users have access to reliable and efficient equipment.
Brand | Key Features | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
Tranter | Wide range, customer focus, strong reputation | |
API | Enhanced surfaces, flexible design, thermal analysis | Engineering expertise, reliability |
Kelvion | Optimized flow, anti-fouling, high-temp resistance | Technical support, quality, customization |
Plate to Plate Heat Exchanger Basics
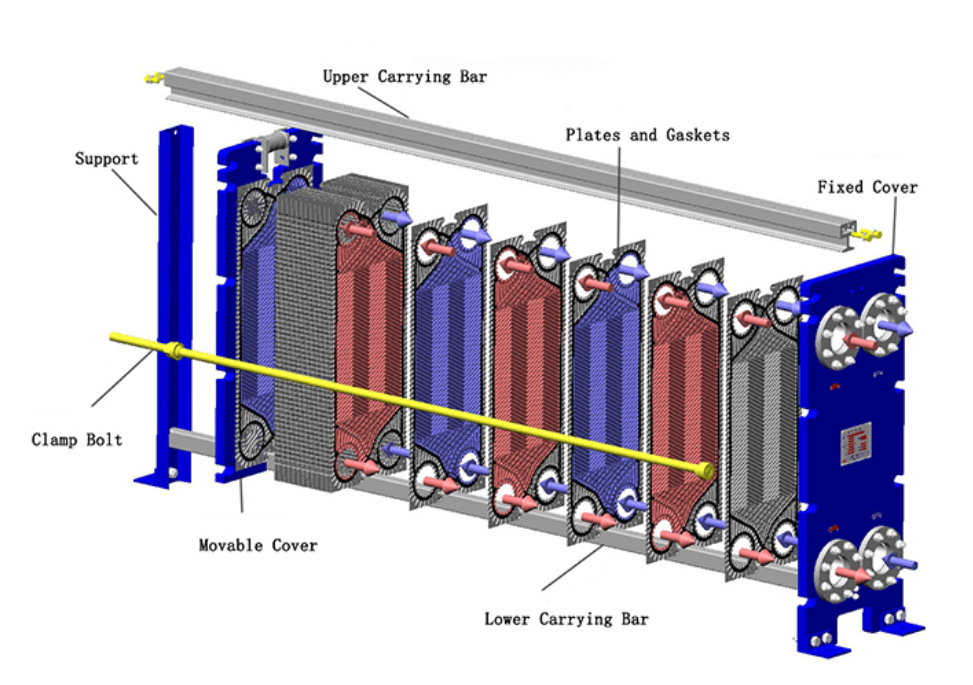
How Plate to Plate Heat Exchangers Work
A plate and frame heat exchanger uses a series of thin, wavy metal plates to transfer heat between two fluids. The design maximizes surface area in a compact space. The counterflow configuration keeps a large temperature difference between the fluids, which increases heat transfer. The herringbone pattern on the plates creates turbulence, improving heat transfer rates and reducing energy waste. This structure allows for effective energy transfer while using less material than other designs. Corrugated plate patterns and optimized flow arrangements further enhance performance by increasing turbulence and reducing dead zones. Advanced sealing mechanisms and gasket materials prevent leaks and make maintenance easier. The use of advanced materials and coatings improves corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
Design Feature | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
Optimized plate geometries | Enhances heat transfer efficiency |
Improved flow distribution | Reduces pressure drop and increases system effectiveness |
Advanced sealing mechanisms | Prevents leaks and ensures proper operation |
Advanced materials and coatings | Contributes to corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity |
Industrial Applications
Plate and frame heat exchangers serve many industrial applications. In HVAC systems, they recover heat from exhaust air, cutting energy use by up to 30%. Power generation plants use them for waste heat recovery from turbines and boilers. The food and beverage industry relies on them for pasteurization, sterilization, and cooling, focusing on hygiene and efficiency. Chemical and petrochemical plants use them for process heating and cooling, where corrosion resistance and energy efficiency matter. Refrigeration and cold chain logistics depend on them for efficient cooling cycles and temperature stability.
Industrial Sector | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|
HVAC Systems | Heat recovery from exhaust air, reducing energy consumption by up to 30%. |
Power Generation | Waste heat recovery from turbines and boilers for additional electricity production. |
Food and Beverage Processing | Pasteurization, sterilization, and cooling processes with a focus on hygiene and efficiency. |
Chemical and Petrochemical Industries | Process heating and cooling with a focus on corrosion resistance and energy efficiency. |
Refrigeration and Cold Chain Logistics | Efficient cooling cycles for cold storage and logistics, supporting temperature stability. |
Note: Plate and frame heat exchangers play a key role in chemical processing plants. Their compact design and high thermal performance help reduce energy waste and operational costs. Consistent temperature control supports productivity and safety in high-temperature operations.
Model Comparison: Efficiency, Cost, and Reliability
Performance and Energy Efficiency
Industrial users often prioritize performance and energy efficiency when selecting a plate to plate heat exchanger. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger delivers high thermal efficiency through its advanced plate patterns and compact design. The model achieves a surface-area density of up to 200 m²/m³, which supports rapid heat exchange and minimizes energy loss. This design leads to a significant boost in heat transfer efficiency, especially in demanding environments.
Other leading brands, such as Tranter, API, and Kelvion, also focus on maximizing thermal efficiency. Tranter’s models use advanced sealing and plate geometry to improve energy efficiency. API emphasizes flexible design and enhanced surfaces, which help maintain high thermal efficiency across various applications. Kelvion’s exchangers feature optimized flow paths that support energy-saving designs and consistent performance.
Real-world data from large-scale installations highlight the impact of these high-efficiency solutions:
Application | Performance Improvement | Location |
|---|---|---|
Power Plants | Asia | |
Chemical Plants | 20% reduction in energy use | Europe |
Large-scale Heating | 25% increase in adoption | Scandinavian countries |
Refineries | 10% boost in throughput | North America |
Food Processing | 30% reduction in cleaning time | New Zealand |
Shanghai Heat Transfer’s model consistently ranks among the top performers in these sectors. Its ability to maintain high thermal efficiency and energy efficiency under variable conditions makes it a preferred choice for industries seeking reliable performance and energy-saving designs.
Note: High thermal efficiency not only reduces operational costs but also supports sustainability goals by lowering energy consumption.
Cost and Maintenance
Cost remains a critical factor for industrial buyers. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger offers cost-effective solutions by combining a compact footprint with easy maintenance features. The modular design allows for quick disassembly, which reduces downtime during cleaning or inspection. Clean-in-Place compatibility further streamlines maintenance, helping facilities minimize labor costs and maximize uptime.
Tranter, API, and Kelvion also provide models with maintenance-friendly features. Tranter’s exchangers use advanced gaskets for fast replacement. API’s flexible frame designs simplify plate access. Kelvion’s anti-fouling surfaces reduce the frequency of cleaning cycles. However, Shanghai Heat Transfer’s focus on low fouling and robust gasket materials often results in lower total cost of ownership over the product’s lifespan.
In food processing plants, for example, users report a 30% reduction in cleaning time when using modern plate to plate heat exchangers. This improvement translates directly into cost savings and increased productivity.
Tip: Facilities that prioritize both efficiency and low maintenance costs often select models with Clean-in-Place compatibility and modular construction.
Reliability and Durability
Reliability and durability determine the long-term value of a plate to plate heat exchanger. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger uses high-grade materials such as stainless steel, titanium, and Hastelloy. These materials withstand harsh chemicals, high temperatures, and pressure fluctuations. The robust gasket options, including nitrile, EPDM, and Viton, ensure a leak-tight seal and prevent cross-contamination.
Other leading brands also emphasize durability. Tranter and API use corrosion-resistant alloys and advanced gasket technology. Kelvion’s exchangers feature reinforced frames and high-temperature resistance. Across the industry, the expected lifespan for plate to plate heat exchangers ranges from 10 to 20 years. Maintenance practices and operational conditions play a significant role in achieving the upper end of this range.
Lifespan Range | Factors Affecting Durability |
|---|---|
10 to 20 years | Maintenance practices |
Operational conditions |
Shanghai Heat Transfer’s commitment to reliable performance ensures that its exchangers deliver consistent results throughout their service life. Many industrial users report stable operation and minimal unplanned downtime, even in challenging environments.
Callout: Selecting a model with proven reliability and robust construction helps facilities avoid costly interruptions and maintain high thermal efficiency year after year.
Choosing the Right Plate to Plate Heat Exchanger
Assessing Your Industrial Needs
Selecting the best plate to plate heat exchanger begins with a clear understanding of the specific requirements of each industrial process. Engineers and facility managers should consider several factors before making a decision:
Temperature difference between fluids
Fluid type and compatibility
Flow rate and pressure limitations
Thermal properties of the plate material
Space constraints within the facility
Maintenance needs and cleaning frequency
Overall cost and budget
A step-by-step approach helps clarify priorities:
Define heat transfer requirements for the process.
Check fluid compatibility with available plate materials.
Measure flow rates and pressure or temperature limits.
Evaluate the risk of fouling and plan for maintenance.
Tip: For high-temperature or high-pressure environments, stainless steel or titanium alloys offer strength and corrosion resistance. In corrosive settings, titanium or Hastelloy plates provide extra durability.
Matching Features to Applications
Different industries require unique features from their heat exchangers. The following table shows how key features align with common applications:
Feature | Food Processing | Power Generation |
|---|---|---|
Supports changing recipes and production needs | Adjusts to different thermal loads | |
Ease of cleaning | Essential for hygiene and contamination control | Important for efficient maintenance |
Specialized plate designs | Smooth channels for hygiene and laminar flow | Designs that boost thermal efficiency |
Material selection | Corrosion resistance for food safety | Handles high-temperature fluids |
Anti-fouling capabilities | Prevents buildup in sensitive processes | Reduces maintenance in energy systems |
A custom-designed plate can address specific challenges, such as hygiene in food processing or efficiency in power generation. By matching features to application needs, industrial users can maximize performance and reliability.
Case Studies and Industry Examples
Shanghai Heat Transfer in Action
Shanghai Heat Transfer’s Gasketted Plate Heat Exchanger has demonstrated strong results in industrial environments. In a large food processing facility, engineers installed the system to improve pasteurization efficiency. The compact design allowed the team to fit the unit into a limited space, while the modular plates made cleaning and maintenance straightforward. Operators reported a 30% reduction in cleaning time and a noticeable drop in energy consumption. The facility also benefited from the exchanger’s ability to handle variable flow rates, which supported changes in production without sacrificing performance.
A chemical plant used the same model to recover waste heat from a high-temperature process. The robust materials resisted corrosion and maintained a leak-tight seal, even under fluctuating pressures. Plant managers noted stable operation and minimal downtime, which helped them meet strict production targets.
Note: Many industrial users value the easy maintenance and high efficiency of Shanghai Heat Transfer’s plate to plate heat exchangers.
Lessons from Other Brands
Industrial users have reported several benefits when using plate to plate heat exchangers from various brands:
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
High Heat Transfer Efficiency | Large surface area and thin plates support efficient heat transfer. |
Compact Size | Space-saving design fits tight installations. |
Versatility | Adapts to different fluids and processes. |
Easy Maintenance | Removable plates simplify cleaning and reduce downtime. |
Energy-efficient | Reduces energy use in daily operations. |
Cost-effective | Lowers installation and operational costs. |
Hygienic and Safe | Sanitary features prevent cross-contamination. |
However, users have also faced challenges during installation and operation:
Fouling and scaling can reduce efficiency and require frequent cleaning.
Leaks and gasket failures sometimes interrupt production.
Corrosion and thermal shock may shorten equipment lifespan.
Wrong sizing or poor flow distribution can cause overheating or vibration.
Managing multi-phase flows and high-pressure applications often requires advanced designs.
Tip: Regular monitoring and proper sizing help industrial facilities avoid common issues and maintain reliable performance.
Decision-makers compare leading brands by reviewing material grade, thermal performance, and pressure ratings. The table below helps guide selection for any plate to plate heat exchanger:
Checklist Item | Description |
|---|---|
Material Grade | Corrosion resistance and compatibility |
Thermal Performance | Efficiency under operating conditions |
Pressure & Temperature Ratings | Suitability for process safety |
Shanghai Heat Transfer offers advanced reliability and efficient solutions for industrial needs.
FAQ
What makes a plate to plate heat exchanger suitable for industrial use?
Engineers select this equipment for its high efficiency, compact design, and ability to handle demanding industrial processes with minimal maintenance.
How often should industrial facilities perform maintenance on these heat exchangers?
Most industrial users schedule inspections and cleaning every six to twelve months to maintain peak performance and prevent fouling.
Can a plate to plate heat exchanger handle different fluid types?
Yes. Manufacturers design these units to work with various fluids, including corrosive or high-temperature liquids, making them versatile for industrial applications.





