Easy Maintenance Tips for Gas Plate Heat Exchangers
Shanghai Heat Transfer designed the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger for durability and top performance. This Gas Plate Heat exchanger uses welded corrugated plates and robust materials to handle tough industrial conditions. Operators will find maintenance easy with openable bolted connections and integrated cleaning systems. Always follow the manufacturer’s manual for safe and efficient operation.
Installation and Inspection for Plate Heat Exchanger
Pre-Installation Safety Steps
Before starting any installation, Shanghai Heat Transfer recommends reviewing the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger installation manual. A detailed construction plan helps organize the process and ensures all technical measures and personnel are in place. Workers should check the dimensional accuracy of each part to avoid improper assembly. Pressure testing confirms the sealing and strength of the unit, making sure all connections remain leak-free.
Tip: Always work in a gas-free area and use proper ventilation to prevent overheating. Install safety devices like pressure relief valves and temperature sensors to protect against abnormal conditions.
The table below highlights common safety incidents during installation:
Safety Incident Type | Description |
|---|---|
Pressure and Temperature Excursions | Can lead to plate deformation, gasket failure, or rupture, releasing hot fluids. |
Thermal Cycling and Fatigue | Causes thermal stress, leading to cracks or warping. |
Leakage | Occurs due to gasket deterioration or improper assembly. |
Fouling | Accumulation of deposits can cause pressure spikes and equipment failure. |
Inspection and Maintenance Challenges | Difficulties in inspection can lead to undetected damage. |
Proper Gasket and Plate Alignment
Correct alignment of gaskets and plates is essential for the plate heat exchanger to function efficiently. Improper assembly can cause leaks, reduce performance, or increase pressure drop. Operators should:
Align plates carefully to prevent internal and external leaks.
Secure all connections according to the manual.
Double-check gasket placement before tightening bolts.
Initial System Checks
After installation, operators should perform several checks to ensure optimal performance. The following table lists key parameters to review:
Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
Pressure Ranges | Check working fluids' pressure and allowable pressure drop. |
Temperature Ranges | Verify temperature ranges for all fluids. |
Fluid Properties | Assess density, viscosity, and thermal conductivity. |
Fouling Tendency | Evaluate risk of deposits forming. |
Flow Ranges | Determine flow rates for different conditions. |
Cooling Medium | Confirm cooling medium availability. |
Space Availability | Ensure enough space for the plate heat exchanger. |
Design Codes | Review codes for minimum velocity and safety. |
Operators should also clean the plates, inspect for defects, perform dye tests for pinholes, and hydro-test the equipment for leaks. These steps help maintain the reliability and safety of the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger.
Maintenance Tips for Gas Plate Heat Exchanger
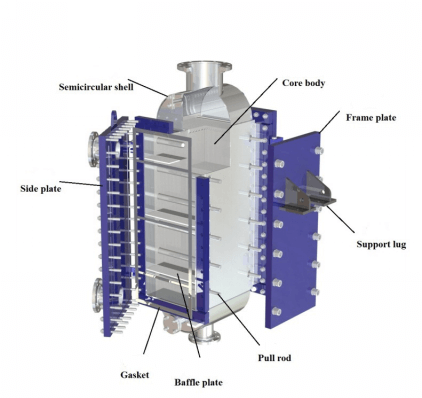
Routine Visual Inspections
Operators should inspect the gas plate heat exchanger regularly to maintain peak performance. Shanghai Heat Transfer recommends a daily inspection system. During each check, staff should look for:
Wet spots or corrosion on the shell, which may signal leaks.
Gasket damage, such as cracks or swelling.
External corrosion on the surface of the unit.
Routine inspections help identify corrosion, leaks, and plate damage early. This practice prevents efficiency loss and supports safe operation. Operators should also listen for unusual noises, such as gurgling or knocking, which may indicate blockages or turbulence inside the gas plate heat exchanger.
Cleaning Procedures and CIP Use
Cleaning-in-Place (CIP) systems simplify the cleaning process for the gas plate heat exchanger. These systems allow operators to remove fouling and scaling without disassembling the unit. The choice of cleaning agent depends on the type of deposit found inside the exchanger. The table below outlines recommended cleaning agents for different fouling types:
Type of Fouling | Recommended Cleaning Agent |
|---|---|
Mineral scale (calcium carbonate) | Mild acids (citric acid, acetic acid) |
Tough deposits | Stronger acids (hydrochloric, sulfuric acid) |
Organic deposits | Alkaline cleaners (sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide) |
Operators may also use inhibited acidic cleaners for mineral scale, alkaline detergents with surfactants for biological fouling, and emulsifying alkaline cleaners for oils and organic films. For mixed fouling, a sequence of cleaning stages ensures thorough removal. Regular cleaning removes deposits that can cause pressure drops and reduced heat transfer efficiency in the gas plate heat exchanger.
Gasket and Plate Care
Proper care of gaskets and plates extends the life of the gas plate heat exchanger. Shanghai Heat Transfer recommends several best practices:
Establish a daily inspection routine for the equipment.
Check the operation status, including the appearance and connection parts.
Address abnormal situations, such as leakage, noise, or vibration, promptly.
Clean and maintain the equipment to prevent dust and impurities from affecting performance.
Operators should use full penetration welds for the first 50 mm from the gasket face to prevent leakage. For hydrogen service, full penetration welds along the entire length help avoid cracking. Welding both sides enhances strength and prevents media ingress. Gasket failure can result from hydraulic hammering, swelling due to incompatible fluids, deformed gasket grooves, insufficient compression, clogging under high pressure, or broken glue bonds. The table below summarizes common causes of gasket failure:
Cause | Description |
|---|---|
Hydraulic hammering | Sudden pressure changes can damage gaskets. |
Gasket swelling | Incompatibility with the media being processed. |
Deformed gasket grooves | Improper sealing and leakage. |
Un-tightened plate pack | Insufficient compression can cause gasket failure. |
Clogging with high pressure | Exacerbates gasket wear and leads to failure. |
Broken glue bond | High pressure can cause adhesive failure, leading to gasket issues. |
Operators should select gasket materials compatible with the fluids processed by the gas plate heat exchanger and avoid excessive pressure or temperature.
Troubleshooting and When to Call a Pro
Several issues may signal the need for professional assistance with a gas plate heat exchanger. Reduced heat transfer efficiency often points to blockages. Increased pressure drop suggests flow restrictions. Unusual noises, such as knocking, may indicate cavitation or turbulence. Frequent maintenance intervals can signal underlying problems, including clogs or internal damage. Visual signs, such as corrosion, scaling, or deposits, may indicate internal issues.
Operators should schedule professional maintenance at least once every six months, even if the gas plate heat exchanger appears to function well. If excessive pressure drop occurs after routine checks, this may indicate fouling that requires unscheduled maintenance. If all other components, such as pipes and pumps, function properly but issues persist, cleaning the heat exchanger becomes necessary.
The table below shows recommended inspection intervals:
Inspection Type | Recommended Interval |
|---|---|
Visual Inspection | At least every 5 years or at the same interval as internal inspection, whichever is less. |
Internal Inspection | Should not exceed half the estimated remaining life or 10 years, whichever is less. |
Corrosion Under Insulation | Consider for insulated vessels exposed to moisture, operating between 25°F and 250°F. |
Routine inspections, cleaning, and pressure testing all contribute to the operational efficiency of the gas plate heat exchanger. These practices help prevent leaks, maintain heat transfer efficiency, and ensure the integrity of welds and seals. Shanghai Heat Transfer provides detailed guidelines to support safe and effective maintenance.
Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger performs best with proper installation and routine care. Operators should:
Follow the manufacturer’s manual for every step.
Inspect and clean the unit regularly.
Seek professional help for complex issues.
Regular maintenance ensures safety, efficiency, and long service life.
FAQ
How often should operators clean the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger?
Operators should follow Shanghai Heat Transfer’s guidelines and perform routine cleaning every six months. More frequent cleaning may be needed for challenging industrial environments.
What signs indicate a need for professional maintenance?
Unusual noises, persistent leaks, or reduced efficiency signal issues. Shanghai Heat Transfer recommends contacting a professional if these problems continue after basic troubleshooting.
Can operators use any cleaning agent for maintenance?
Operators should only use cleaning agents approved by Shanghai Heat Transfer. Using the wrong agent can damage plates or gaskets and reduce equipment lifespan.






