How Do Gas to Gas Plate Heat Exchangers Transfer Heat
How Do Gas to Gas Plate Heat Exchangers Transfer Heat
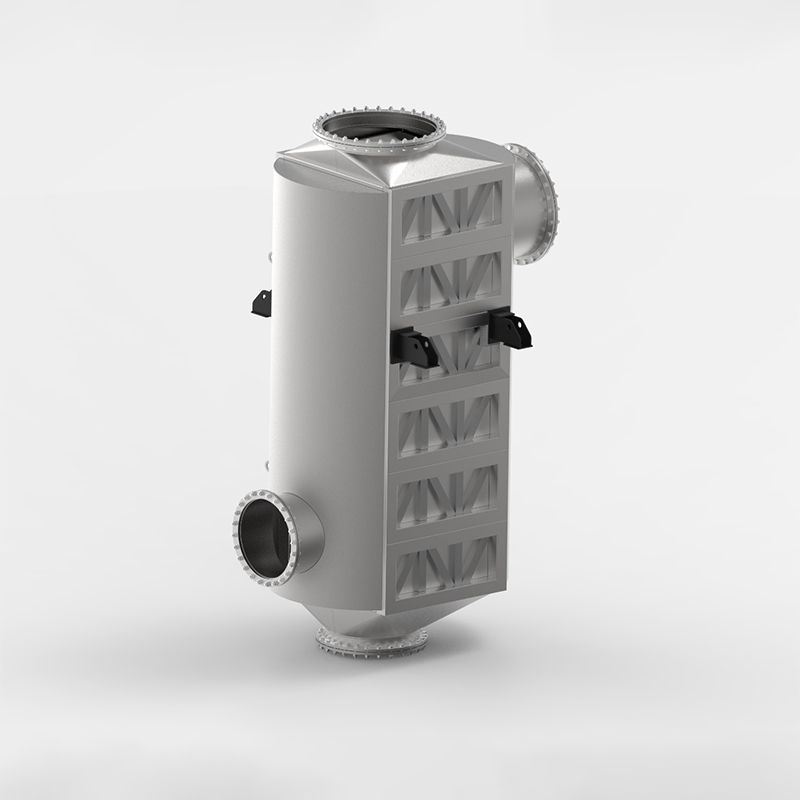
A gas to gas plate heat exchanger uses a series of metal plates to move heat from hot exhaust gases to cooler incoming air. This process allows factories to capture waste heat and reuse it, which boosts energy efficiency. The Plate Air Preheater from Shanghai Heat Transfer stands out in this field. Its design ensures that heat passes quickly and evenly between gases, helping industries recover more heat and reduce fuel use. Efficient heat transfer leads to lower costs and supports cleaner operations.
Gas to Gas Plate Heat Exchanger Basics
What Is a Gas-to-Gas Plate Heat Exchanger
A gas-to-gas plate heat exchanger transfers heat between two separate gas streams. This device uses a series of thin metal plates to create channels for hot and cold gases. The hot gas flows on one side of each plate, while the cold gas moves on the other side. The plates act as barriers, so the gases never mix. Heat moves from the hotter gas to the cooler gas through the plate walls. This process relies on thermal conduction and convection. The movement of gases along the channels helps carry thermal energy into and out of the heat exchanger.
The main part of a gas to gas plate heat exchanger is the plate bundle. As flue gas enters the heat exchanger, it gives up heat to the plates. The other gas stream absorbs this heat, which raises its temperature. This method helps factories recycle energy and lower emissions. The plate heat exchanger uses micro-channels formed by the plates. These channels allow for efficient heat transfer without mixing the gases.
Plate Heat Exchanger Design
The design of a gas-to-gas plate heat exchanger plays a key role in its efficiency. Most plate heat exchangers use corrugated plates. These plates create turbulence in the gas streams, which increases the heat transfer rate. The shape of the corrugation affects how the gas flows, the amount of turbulence, and the pressure drop. All these factors help improve heat exchange.
Manufacturers use different materials for the plates based on the application. Common choices include:
Stainless steel, which offers durability.
Titanium, which resists corrosion in salty or harsh environments.
Hastelloy, which works well with corrosive chemicals.
Some plate heat exchangers use advanced designs like CurveFlow. This design spreads the gas evenly across the plate width. It can boost heat transfer efficiency by up to 15% compared to traditional designs. The right design and material choice ensure that the gas-to-gas plate heat exchanger works well in many industries.
Heat Transfer Process
Gas Flow Channels
Gas-to-gas plate heat exchangers use a series of narrow channels to guide hot and cold gases through the unit. Each channel sits between two plates, forming a path for the gases to flow. The hot gas enters one set of channels, while the cold gas enters the alternate set. The plates keep the gases separate, but allow heat to move from the hot side to the cold side. This setup increases the contact area between the gases and the metal plates, which boosts heat transfer.
The design of these channels affects both heat transfer and pressure drop. Increasing the area for heat exchange improves heat transfer, but it also makes the flow path longer. This can lead to a higher pressure drop, which means the system needs more energy to push the gases through. Engineers must find a balance between maximizing heat transfer and keeping the pressure drop low. They often adjust the size and shape of the channels to optimize performance. Turbulence inside the channels helps mix the gases and improves heat transfer, but it can also increase resistance to flow.
Note: Careful design of gas flow channels helps high-efficiency gas-to-gas plate heat exchangers achieve strong heat recovery while keeping energy use in check.
Main Mechanisms of Heat Transfer
The heat transfer process in a gas-to-gas plate heat exchanger relies on three main mechanisms. The table below explains each one and its role in heat exchangers:
Mechanism | Description | Role in Heat Exchangers |
|---|---|---|
Conduction | Heat transfer through a solid material. | Heat moves through the walls or surfaces separating the fluids, allowing heat to be transferred from hot to cold fluid. |
Convection | Transfer of heat between a solid surface and a moving fluid. | Heat is transferred from the hot fluid to the heat exchanger surface and then to the cold fluid. |
Radiation | Transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves. | Plays a minor role in specific high-temperature applications, less significant in most heat exchangers. |
Counterflow and Crossflow Configurations
The arrangement of gas flow in a gas-to-gas plate heat exchanger can follow different patterns. The two most common are counterflow and crossflow configurations. In a counterflow design, the hot and cold gases move in opposite directions. This setup creates a large temperature difference across the plates, which leads to superior heat transfer. Counterflow heat exchangers are compact and offer high thermal efficiency, making them ideal for applications where maximum heat recovery is needed. However, they require careful flow management and can have higher pressure drops.
In a crossflow design, the gases move at right angles to each other. This arrangement is easier to customize and works well for certain specialized applications. Crossflow heat exchangers are less thermally efficient than counterflow designs, but they can be optimized with baffles to improve performance. The choice between counterflow and crossflow depends on the needs of the process, the desired heat transfer efficiency, and the acceptable pressure drop.
Configuration | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Counterflow | Superior heat transfer, Compact design, Energy savings | More complex flow management, Potentially higher pressure drop, Not always the best fit |
Crossflow | Effective in gas-liquid heat transfer, Customizable with baffles | Less thermally efficient than counter flow, Ideal for specialized applications only |
Uniform flow distribution is important for both configurations. If the flow is not even, the heat exchanger may lose efficiency and experience higher pressure drops. Parallel flow designs are less sensitive to uneven flow, while counterflow designs need more careful management to maintain high performance.
Corrugated Plate Structure
The plates inside a gas-to-gas plate heat exchanger often have a corrugated or wavy surface. This structure plays a key role in the heat transfer process. Corrugations create turbulence as the gases move through the channels. Turbulence breaks up smooth, laminar flow and mixes the gases more thoroughly. This mixing increases the rate of heat transfer from the hot gas to the plate and from the plate to the cold gas.
Corrugated plates also help optimize the geometry of the channels. By adjusting the pattern and depth of the corrugations, engineers can control the level of turbulence and the pressure drop. More turbulence usually means better heat transfer, but it can also make it harder for the gases to flow. The right design balances these effects to achieve high heat transfer efficiency.
Corrugated plates promote controlled turbulence, which boosts heat transfer performance.
Turbulence-inducing structures disrupt laminar flow, leading to better mixing and higher heat transfer coefficients.
Optimizing the channel geometry and surface features can further improve turbulence and thermal efficiency.
Gas-to-gas plate heat exchangers use these design features to maximize heat transfer while keeping energy use and maintenance needs low. The combination of well-designed flow channels, the right flow configuration, and advanced plate structures allows these heat exchangers to deliver reliable and efficient heat recovery in many industrial settings.
Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Energy Recovery Benefits
Gas to gas plate heat exchangers play a major role in energy recovery. These devices capture waste heat from exhaust gases and transfer it to incoming air. This process increases the temperature of the air before it enters the system. As a result, less energy is needed to reach the desired temperature. Plate heat exchangers use thin metal plates to maximize the surface area for heat transfer. This design allows for high heat transfer efficiency with minimal material.
Plate heat exchangers boost plant performance by:
Achieving high heat transfer efficiency.
Reducing energy consumption through effective heat recovery.
Lowering the use of resources and supporting sustainable operations.
Plants that use plate heat exchangers see a direct improvement in overall efficiency. They recover more heat from exhaust gases and use less fuel to power their processes.
Reducing Fuel Consumption
Heat exchangers help factories cut fuel use by making the most of every bit of heat. When heat exchangers recover heat from exhaust gases, they preheat the air or gas entering the system. This means the burners or heaters need less fuel to reach operating temperatures. Over time, this leads to significant savings. Plate heat exchangers also reduce the strain on equipment, which can lower maintenance costs.
Operators notice that heat exchangers keep the process stable. The steady supply of preheated air helps maintain consistent temperatures. This stability improves product quality and reduces the risk of equipment failure. By using heat exchangers, companies can meet production goals while spending less on fuel.
Lowering Emissions
Heat exchangers support cleaner operations by lowering emissions. When factories use less fuel, they release fewer greenhouse gases. Plate heat exchangers make this possible by capturing and reusing heat that would otherwise escape into the atmosphere. This process not only cuts carbon emissions but also reduces thermal pollution.
Many industries choose plate heat exchangers to meet strict environmental rules. These devices help companies lower their environmental impact and support sustainable practices. Heat exchangers also minimize the release of particulates and other pollutants. By improving heat recovery, they make industrial processes safer for workers and the environment.
Applications and Brand Advantages
Industrial Uses
Many industries rely on plate heat exchanger technology to recover heat and improve efficiency. Industrial gas-to-gas plate heat exchangers play a key role in sectors that handle large volumes of process gases. The table below shows where these heat exchangers make the biggest impact:
Sector | Applications |
|---|---|
Oil and Gas Processing | High temperature recuperation, gas dew point control, recovery of natural gas liquids, liquefaction and regasification of LNG. |
Chemical and Industrial Gas | Performance efficiency improvement, environmental impact reduction, safety enhancement, and cost savings through reduced coolant flows. |
These sectors use plate heat exchanger systems to manage heat, reduce energy waste, and meet strict environmental standards.
Choosing the Right Plate Heat Exchanger
Selecting the best plate heat exchanger for an application requires careful planning. Engineers consider several important factors:
Process requirements such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and heat load.
The type of fluids involved, including their corrosiveness and viscosity.
Thermal efficiency, which depends on the design, flow arrangement, and material conductivity.
Space constraints and the need for flexible installation.
Maintenance and cleaning needs, including resistance to fouling.
Compliance with industry safety and quality standards.
A well-chosen plate heat exchanger matches the process needs and delivers reliable heat recovery.
Shanghai Heat Transfer Brand
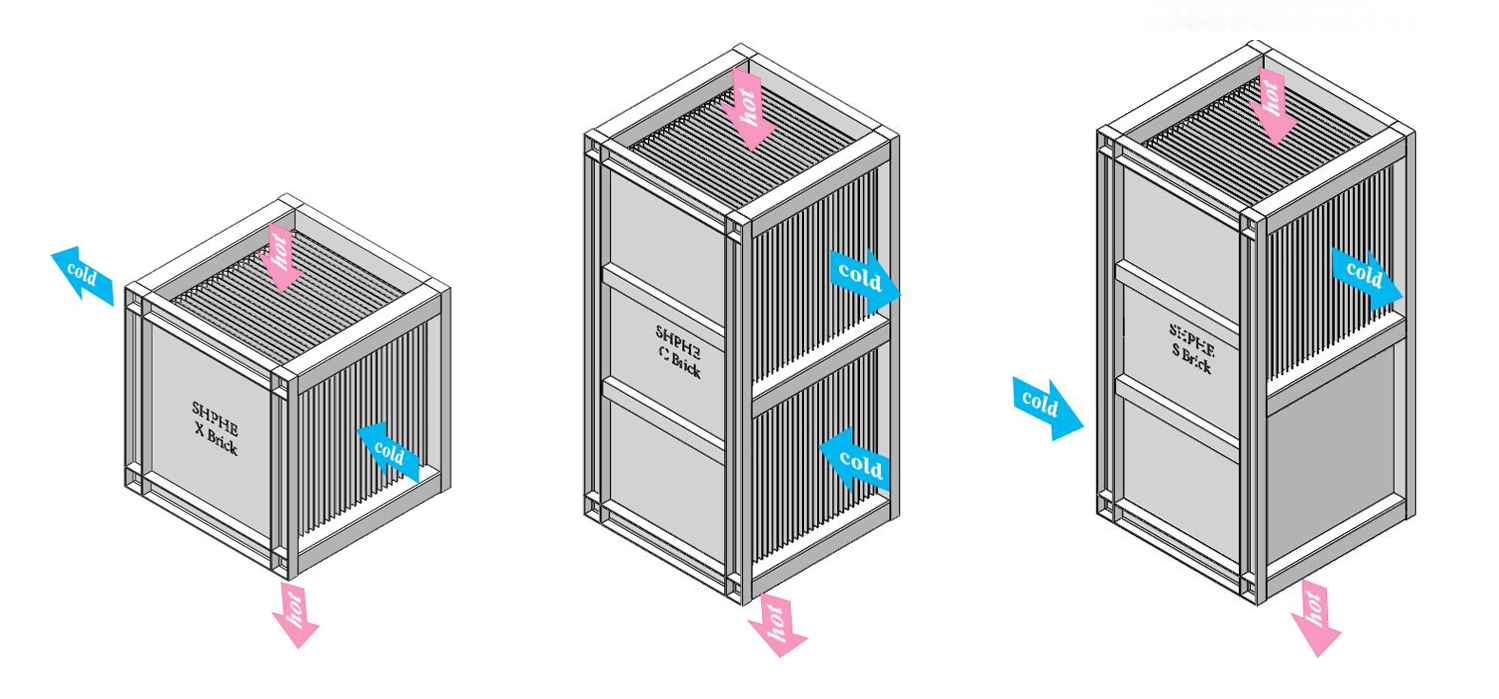
Shanghai Heat Transfer stands out as a trusted provider of plate heat exchanger solutions. The Plate Air Preheater features a modular design that brings several advantages:
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Flexibility in structure | The modular design allows for adaptable installation in various industrial settings. |
Enhanced heat transfer performance | The design contributes to higher efficiency in heat transfer, improving overall system performance. |
Ease of maintenance | The compact structure and design reduce dust accumulation, making cleaning and maintenance simpler. |
The Plate Air Preheater uses durable materials and advanced design to ensure long service life. It also supports environmental goals. The product has earned ISO 14001, ISO 9001, and OHSAS 18001 certifications, which show a commitment to quality, safety, and environmental management.
Shanghai Heat Transfer offers reliable plate heat exchanger technology for industries that demand high performance and sustainability. Their focus on modular design, durability, and environmental responsibility makes them a top choice for heat recovery solutions.
Gas to gas plate heat exchangers use thin, corrugated plates to create channels that maximize heat transfer between hot and cold gases. These systems boost energy efficiency and support environmental protection by capturing and reusing excess heat, which lowers fuel use and emissions. Facilities benefit from features like modular design and high heat transfer efficiency. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s Plate Air Preheater stands out for its advanced technology and reliable performance, making it a smart choice for industries seeking to recover more heat and operate sustainably.
FAQ
How does a gas-to-gas plate heat exchanger prevent gas mixing?
The plates inside the exchanger create separate channels for each gas stream. These channels keep the hot and cold gases apart. Only heat passes through the plate walls, so the gases never mix.
What industries use the Plate Air Preheater from Shanghai Heat Transfer?
Industries such as oil and gas, metallurgy, and chemical processing use the Plate Air Preheater. These sectors need efficient heat recovery and value energy savings.
Why is modular design important in plate heat exchangers?
Modular design allows easy expansion or reconfiguration. Maintenance becomes simpler because workers can replace individual modules without stopping the whole system. This design also adapts to different space requirements.
How does using a plate heat exchanger help the environment?
Plate heat exchangers recover waste heat and reduce fuel use. This process lowers greenhouse gas emissions and supports cleaner industrial operations.