5 key roles of plate heat exchanger gaskets.
Plate heat exchanger gaskets perform 5 key roles: ...
More
What is a Cold Plate Heat Exchanger?A cold plate heat exchanger is a highly efficient thermal management device designed to absorb and dissipate heat from high-power electronic components, such as CPUs, GPUs, power converters, and laser diodes, by utilizing a liquid coolant circulated through internal channels. Unlike traditional air cooling, cold plates directly contact the heat source, providing superior heat transfer capabilities. They are typically constructed from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, and can be customized with various internal channel designs—including serpentine, parallel, or micro-channel configurations—to optimize flow and thermal performance. Cold plates are integral in applications where precise temperature control is critical, including electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, aerospace avionics, and data centers. For instance, in EVs, cold plates manage battery thermal loads, maintaining optimal temperatures between 15°C to 35°C to ensure safety and longevity. According to industry analyses, the global cold plate heat exchanger market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.5% from 2023 to 2030, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient cooling in electronics and electric mobility. Their ability to handle heat fluxes exceeding 500 W/cm² in concentrated areas makes them indispensable in modern high-density power systems.
How Cold Plate Heat Exchangers WorkCold plate heat exchangers operate on the principle of convective heat transfer, where a liquid coolant (e.g., water, glycol mixtures, or dielectric fluids) absorbs thermal energy from a hot surface and transports it away to a secondary cooling system. The process begins when the cold plate is mounted directly onto the heat-generating component, ensuring maximal thermal contact via thermal interface materials (TIMs). As the coolant flows through precision-engineered internal channels, it captures heat through forced convection. The design of these channels—often optimized using computational fluid dynamics (CFD)—minimizes pressure drop while maximizing turbulence and surface area contact, enhancing heat absorption. For example, micro-channel cold plates can achieve heat transfer coefficients over 10,000 W/m²K, significantly outperforming traditional methods. The heated coolant then circulates to a remote heat exchanger (e.g., a radiator or chiller), where it rejects heat to the ambient environment or a secondary loop before recirculating. In practical applications, such as in data centers, cold plates integrated into server racks can reduce cooling energy usage by up to 30% compared to air conditioning, as reported by studies from the U.S. Department of Energy. This closed-loop system ensures precise temperature control, often maintaining deviations within ±1°C, critical for semiconductor reliability and performance.
Select the most popular foreign trade service products to meet your diverse needs
Learn more about the dynamics and professional knowledge of the foreign trade industry
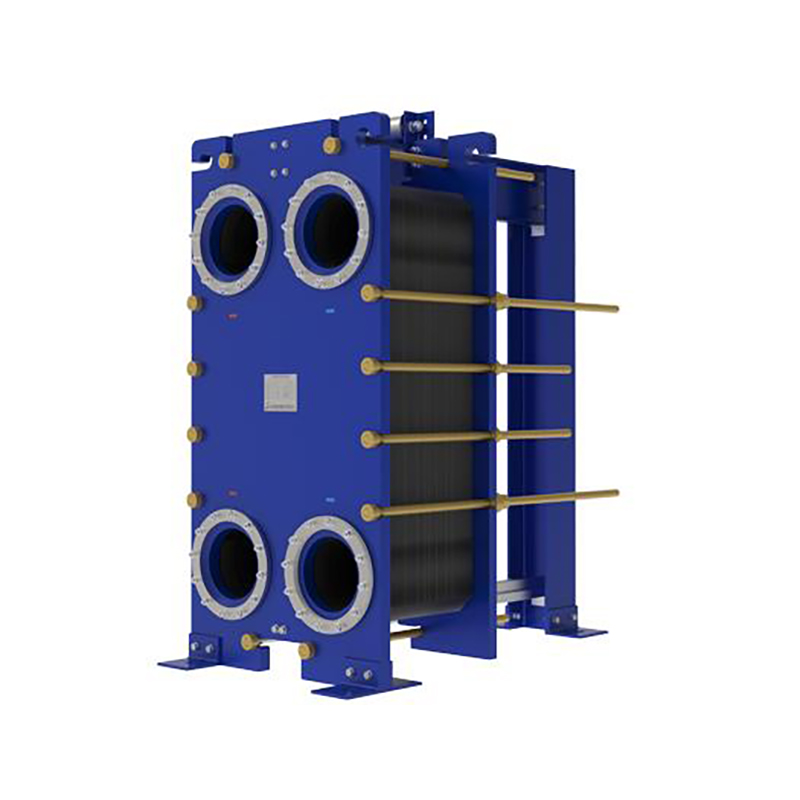

Plate heat exchanger gaskets perform 5 key roles: ...
More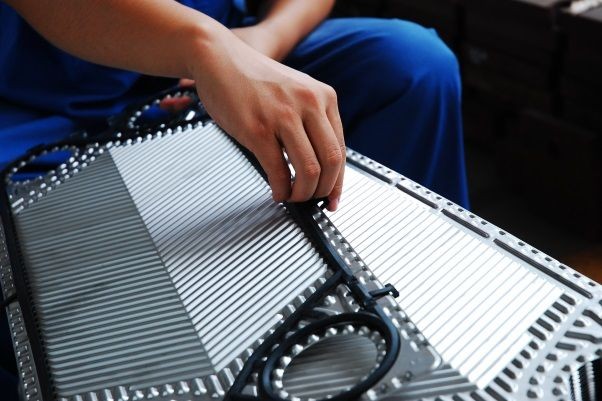
API 662 defines standards for plate heat exchanger...
More
Compare top frame plate heat exchanger models for ...
More
You can see clear differences between welded block...
More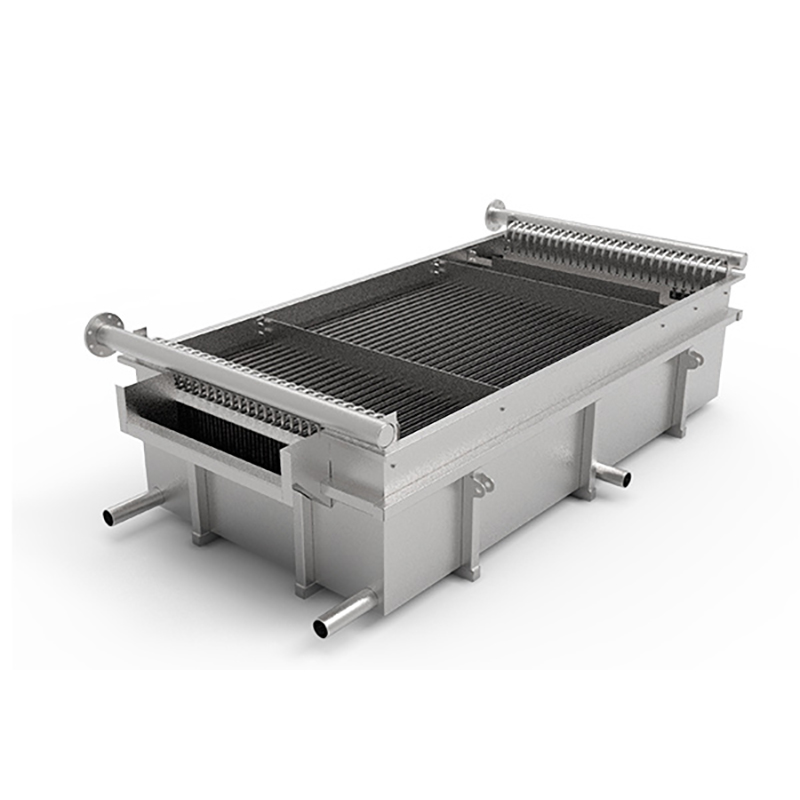
The dimple plate heat exchanger, also known as the...
More
A gasket in heat exchanger seals surfaces, blocks ...
MoreSelect the most popular foreign trade service products to meet your diverse needs
Explore more content related to foreign trade services

User Comments
Service Experience Sharing from Real Customers
Michael Chen
Mechanical EngineerThis cold plate heat exchanger is exceptionally efficient for our high-power electronics cooling application. The thermal performance exceeded our expectations and the build quality is robust.
Sarah Johnson
HVAC Systems DesignerWe integrated this unit into a commercial building's liquid cooling system. The compact design saved significant space and its reliability has been flawless for over six months of continuous operation.
David Williams
Research and Development LeadAn excellent product for our lab's prototype testing. The heat transfer coefficients are impressive. We took off one star purely due to a longer than expected lead time for delivery, but the product itself is top-tier.
Lisa Rodriguez
Plant Engineering ManagerDeployed these heat exchangers on our laser cutting machinery. They have drastically reduced downtime due to overheating and have handled the thermal load perfectly. A critical and reliable component for our manufacturing process.