Comparing Steam Plate Heat Exchangers and Shell and Tube Designs
Selecting the right heat exchanger for steam applications depends on several factors. Users often consider purpose, operating conditions, fluid properties, and pressure drop. Maintenance, available space, and cost also play important roles. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger combines durability and high performance, making it ideal for demanding environments where a steam plate heat exchanger is needed.
Overview of Heat Exchanger Types
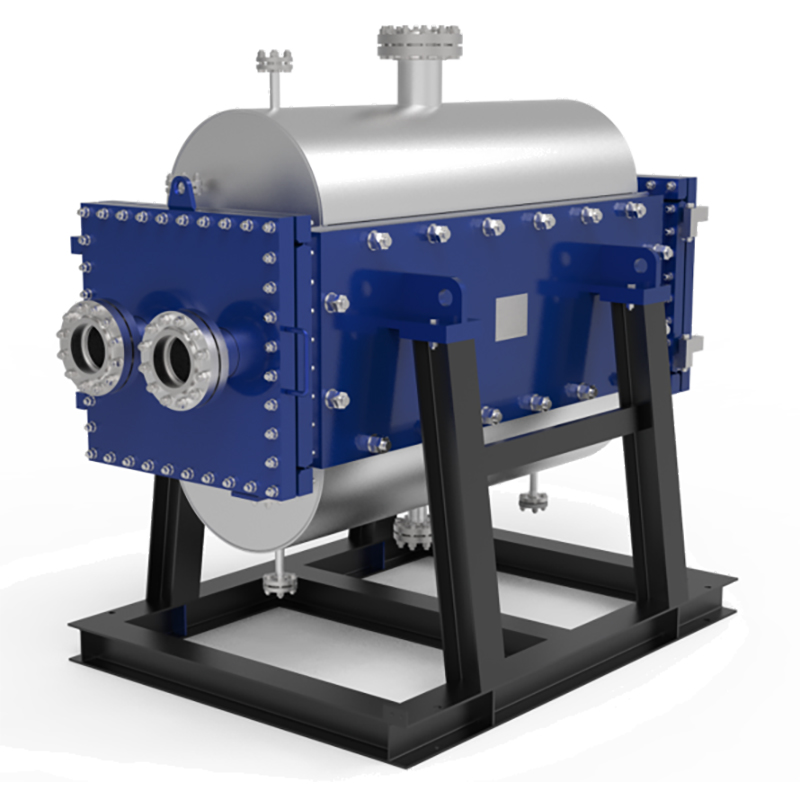

Shanghai Heat Transfer stands out in the industry with its innovative TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger. This hybrid solution combines the strengths of both plate heat exchanger and shell and tube designs. It delivers high heat transfer efficiency and robust performance, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Steam Plate Heat Exchanger Basics
A steam plate heat exchanger uses a series of plates to separate fluids. The plates often have enhanced surfaces, such as embossing, to increase the area for heat transfer. This design allows for efficient energy exchange and a compact footprint. Steam plate heat exchangers are common in industries that require rapid temperature changes and high energy performance, such as food processing and chemical manufacturing.
Shell and Tube Design Basics
Shell and tube heat exchangers feature tubes housed within a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows inside the tubes, while another moves around them within the shell. This arrangement supports a wide range of flow patterns, including parallel and counterflow. Shell and tube designs handle high pressures and temperatures, making them a popular choice in petrochemical and power generation sectors. The shell and tube heat exchanger is valued for its durability and versatility.
Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger Features
A plate and frame heat exchanger consists of rectangular plates held together by end members. Gaskets direct the flow of fluids between the plates. This design allows for easy disassembly and cleaning, which is important in industries where hygiene is critical. The plate and frame exchanger design offers flexibility and can be adapted for different process requirements. Some models use welded plates for added safety and reliability.
Type of Heat Exchanger
Construction Details
Operational Characteristics
Plate Heat Exchangers
Utilize plates to separate fluids, often with enhanced surfaces like fins or embossing.
High surface area to volume ratio, suitable for multiple streams, used in food and chemical industries.
Plate and Frame Heat Exchangers
Comprise rectangular plates held by end members, with gaskets for fluid flow arrangement.
Easily disassembled for cleaning, potential for leakage due to gaskets, can be welded for safety.
Shell and Tube Exchangers
Consist of tubes within a cylindrical shell, allowing fluid flow inside and outside the tubes.
Can handle single or two-phase fluids, flow arrangements can be parallel or counterflow, widely used in petrochemical applications.
The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer bridges the gap between these types. It offers the compactness and efficiency of a plate and frame exchanger with the strength and reliability of a shell and tube. This makes it ideal for applications that demand high heat transfer rates, easy maintenance, and superior energy performance.
Pressure Handling Comparison
Steam Plate Heat Exchanger Pressure Limits
Pressure handling is a critical factor when selecting a heat exchanger for steam applications. The ability to withstand high pressures ensures safe operation and reliable performance. Steam plate heat exchangers are designed to meet the demands of many industrial processes. Their construction uses high-quality metals and precise engineering to achieve impressive pressure ratings.
Steam plate heat exchangers can handle pressures up to 40 bar (580 PSI).
The maximum allowable working pressure depends on the thickness and composition of the metal used.
This robust pressure capacity allows steam plate heat exchangers to perform well in industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and district heating. The compact design also helps maintain high energy efficiency while managing demanding operating conditions. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger takes this a step further by combining the pressure resistance of traditional shell and tube designs with the efficiency of plate technology. This hybrid approach ensures reliable performance even in challenging environments.
Shell and Tube Pressure Performance
Shell and tube heat exchangers have long been the standard for applications that require high pressure and temperature resistance. Their design features a bundle of tubes enclosed within a cylindrical shell. This structure distributes pressure evenly and allows for safe operation at elevated levels.
Shell and tube exchangers can operate at pressures that often exceed those of standard plate and frame units. Many industrial models are rated for pressures above 600 PSI, making them suitable for power generation, petrochemical processing, and heavy industry. The shell and tube heat exchanger also offers flexibility in material selection, which allows engineers to match the equipment to specific process requirements.
Note: Plate and frame heat exchangers, another common type, can handle pressures up to 450 PSI and operate in a wide temperature range. Special gaskets can extend their temperature limits even further.
When comparing performance, both steam plate heat exchangers and shell and tube designs offer strong pressure handling. The choice depends on the specific needs of the application, including the required pressure rating, available space, and desired energy efficiency. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger provides a reliable solution for users who need both high pressure resistance and efficient heat transfer in one compact unit.
Thermal Efficiency
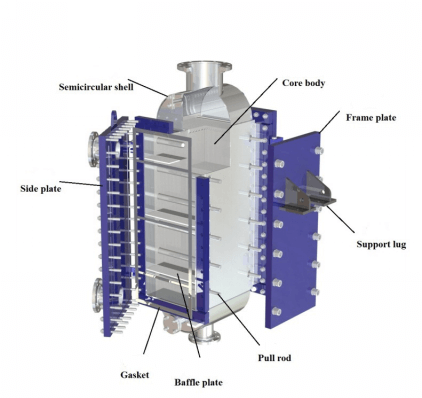
Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger Efficiency
Plate and frame heat exchangers are known for their outstanding heat transfer efficiency. Their design uses thin, corrugated plates that create turbulent flow, which increases the rate of heat transfer between fluids. This turbulence helps prevent fouling and keeps the surfaces clean, which maintains high performance over time. The compact arrangement of plates also means that a large surface area fits into a small space, allowing for rapid energy exchange.
Plate and frame heat exchangers achieve higher overall heat transfer coefficients compared to shell and tube designs.
The plate and frame exchanger minimizes bypassing issues, which enhances flow separation and maximizes heat transfer efficiency.
The design supports efficient heat transfer even at lower flow rates, making it suitable for applications where precise temperature control is important.
Many industries choose plate heat exchanger technology when they need high heat exchanger efficiency and reliable performance. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer builds on these strengths. It combines the efficiency of a plate and frame heat exchanger with the durability needed for challenging industrial environments. This hybrid solution is ideal for processes that require both high performance and easy maintenance.
Shell and Tube Efficiency
Shell and tube heat exchangers have a different approach to heat transfer. They use a bundle of tubes inside a shell, with one fluid flowing through the tubes and another around them. This design is robust and can handle high pressures and temperatures. However, the shell side of tubular exchangers is less efficient thermally. The flow patterns in the shell can lead to areas where heat transfer is not as effective, and pressure drops can occur without significant heat transfer benefits.
Shell and tube exchangers often require a larger footprint to achieve the same performance as plate-based designs.
The design can result in lower heat transfer coefficients, especially when compared to plate and frame exchangers.
Maintenance and cleaning can be more challenging, which may affect long-term performance.
Despite these factors, shell and tube exchangers remain popular in industries that need reliable operation under extreme conditions. Their ability to handle a wide range of fluids and temperatures makes them a versatile choice. For users who want the best of both worlds, the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer offers a unique solution. It delivers the high heat transfer efficiency of plate technology with the strength and reliability of traditional shell and tube designs.
Note: Choosing the right heat exchanger depends on the specific needs of your process. Consider the type of fluids, required performance, and available space to make the best decision.
Maintenance and Cleaning
Steam Plate Heat Exchanger Maintenance
Steam plate heat exchangers are designed for efficient operation and easy maintenance. Many models, such as the plate and frame heat exchanger, allow for quick disassembly, which helps with routine inspections and cleaning. Some advanced designs, like the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer, feature integrated Cleaning-in-Place (CIP) systems. These systems let operators clean the unit without taking it apart, reducing downtime and labor costs. Regular cleaning helps maintain high heat transfer efficiency and prevents fouling. While there is no industry-standard maintenance interval for steam plate heat exchangers, most users schedule inspections based on process conditions and fluid quality.
Heat Exchanger Type | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
Shell and Tube | 1 to 3 years | Depends on operating conditions and fluid types. Longer intervals due to robust construction. |
Steam Plate | N/A | No specific information available. |
Shell and Tube Maintenance
Shell and tube heat exchangers require periodic maintenance to ensure reliable performance. The typical maintenance interval ranges from one to three years, depending on the type of fluid and operating environment. Cleaning methods for shell and tube heat exchangers include:
Chemical cleaning
Pressurized water cleaning
Mechanical techniques, such as rotary cleaning or drilling out deposits
Several factors affect cleaning frequency and downtime:
Design heat transfer coefficient and allowable fouling resistance
Monitoring of performance indicators, such as pressure drop and heat transfer rate
Proper maintenance keeps the shell and tube heat exchanger running efficiently. For users seeking easier cleaning and reduced downtime, the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer offers a modern alternative with advanced cleaning features.
Footprint and Installation
Plate and Frame Space Needs
Plate and frame heat exchangers are known for their compact design. Their thin plates, usually between 0.4 and 0.8 mm thick, allow for a large heat transfer area in a small footprint. This design means that plate heat exchangers often require only about one-tenth the floor space of traditional shell and tube units. The lighter weight—about one-fifth that of a comparable shell and tube exchanger—makes handling and installation much easier.
Plate heat exchangers are designed to be both compact and versatile. This reduces installation space and lowers transportation and installation costs.
Heat Exchanger Type | Installation Space Required | Weight Comparison |
|---|---|---|
Plate and Frame | Less than shell and tube | Weighs less than 1/16th |
Shell and Tube | More space required | Heavier than plate units |
For facilities with limited space, such as commercial buildings or retrofits, plate and frame units offer a clear advantage. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger builds on this benefit, providing high efficiency in a compact, easy-to-install package.
Shell and Tube Space Needs
Shell and tube heat exchangers have a larger footprint. Their tube thickness, typically 2.0 to 2.5 mm, and robust shell construction add significant weight. These units often require more floor space and heavier support structures. The larger size can increase shipping and installation costs.
Shell and tube exchangers are heavier and bulkier than plate units.
They may need special lifting equipment during installation.
Despite the larger footprint, shell and tube designs remain popular in industries where space is less of a concern and durability is a priority.
Expandability and Flexibility
Plate and Frame Scalability
Plate and frame heat exchangers offer impressive scalability. Users can increase capacity by adding flow plates in pairs, which keeps the honeycomb pattern uniform and effective. This modular approach allows facilities to respond quickly to changing process demands. The design supports easy addition or removal of plates, so operators can expand or reduce heat transfer capacity as needed. This flexibility makes plate and frame exchangers a popular choice in industries where production volumes may fluctuate. Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger builds on this concept, providing a solution that combines high performance with the ability to adapt to future requirements.
Shell and Tube Adaptability
Shell and tube heat exchangers are known for their adaptability. Engineers can modify these units in several ways to meet evolving process needs:
Adjust tube and shell configurations to increase the heat transfer coefficient.
Lengthen tubes or enlarge the shell diameter to boost surface area.
Use counterflow arrangements to enhance effectiveness.
The table below highlights common adaptation methods:
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Material Selection | Choose materials for tubes and shells to withstand specific conditions. |
Tube Geometry Adjustment | Change tube diameter and length to optimize heat transfer. |
Baffle Customization | Design baffles to control fluid flow and improve performance. |
Surface Area Increase | Extend tube length or shell diameter for greater heat exchange. |
Configuration Adjustments | Implement counterflow or multiple shell setups for better results. |
Shell and tube exchangers can adapt to changes in process conditions, making them suitable for facilities with evolving requirements. For those seeking a blend of flexibility and robust construction, Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger stands out as a reliable choice for both current and future needs.
Cost Analysis
Initial Investment
The initial investment for a heat exchanger depends on several factors. Shell and tube units often have a lower upfront price, especially for standard designs. Their construction uses common materials and established manufacturing methods. However, installation can require more space and heavier support structures, which may add to the total cost. Plate heat exchanger systems, including plate and frame models, usually have a higher purchase price per unit area. Their compact design and lighter weight can reduce installation expenses. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer offers a balance between initial investment and long-term value, combining robust construction with efficient heat transfer.
Operating Costs
Operating costs play a major role in the total expense of a heat transfer system. Over a 10-year period, plate and frame heat exchangers typically incur lower operating costs than shell and tube designs. This advantage comes from faster installation, easier maintenance, and better energy efficiency. Shell and tube systems may seem less expensive at first, but their maintenance and space requirements can lead to higher costs over time. Plate and frame heat exchanger cost savings become clear when considering reduced downtime and lower energy use. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger provides additional value by offering efficient heat transfer and simplified cleaning, making it a smart choice for facilities focused on long-term savings.
Summary Table of Key Differences
Quick Reference Points
Choosing the right heat exchanger depends on several important factors. The following tables provide a clear comparison of the main types used in steam applications. These quick reference points help users identify which design best fits their needs.
Tip: Consider both performance and practicality when selecting a heat exchanger for your facility.
Heat Exchanger Type | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
Plate Heat Exchanger | High overall heat transfer coefficient, compact design, effective turbulence generation | Cost-effective for specific applications, but limited in customizability compared to others |
Shell and Tube Exchanger | Customizable capacity, suitable for high-pressure applications | Versatile design, can handle a wide range of operating conditions |
Plate and Frame Exchanger | Mass-produced plates, efficient heat transfer, lower fouling potential | Less flexible in design compared to shell and tube, but often more efficient in operation |
Below is a summary of the main advantages and disadvantages for each type:
Heat Exchanger Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Shell & Tube | Widely used, rugged, versatile, handles high pressures and temperatures | Lower thermal efficiency, possible flow issues, larger footprint |
Compact (Plate) | Low cost, high heat transfer, small footprint, lower fouling | Limited pressure range, potential for plugging, careful material selection needed |
Air Cooled | Good for water-scarce areas, low maintenance, handles high temperatures | High initial cost, large space needed, higher outlet temperatures |
Plate and frame exchangers offer high efficiency and easy maintenance.
Shell and tube units provide durability and adaptability.
For demanding or space-limited applications, Shanghai Heat Transfer’s TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger delivers a unique blend of efficiency, strength, and flexibility.
Application Recommendations
Industrial Steam Uses
Industrial steam systems demand reliable heat transfer and robust construction. The shell and tube heat exchanger remains a standard in many sectors due to its adaptability and strength. Common applications include:
Power generation—condensers and feedwater heaters.
Oil and gas—crude oil cooling and gas processing.
Chemical processing—distillation, evaporation, and condensation.
Food processing—gentle heating and cooling, such as milk pasteurization.
Waste heat recovery—capturing byproduct energy.
Automotive and aerospace—engine cooling and hydraulic systems.
For processes involving challenging fluids or extreme conditions, the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer offers high temperature capability, pressure resistance, and corrosion-resistant materials. This makes it a strong choice for demanding industrial environments.
Commercial and HVAC Uses
Commercial and HVAC systems often require compact, efficient solutions. The table below compares common heat exchanger types for these settings:
Heat Exchanger Type | Description | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
Shell and Tube | Durable and versatile | Oil and gas, power generation, chemical industries |
Plate | Compact and efficient, ideal for limited space | HVAC systems, food processing, waste heat recovery |
A plate and frame heat exchanger is often selected for its efficiency and ease of maintenance in HVAC and commercial buildings.
Space-Limited Installations
Space constraints influence heat exchanger selection. Key considerations include application, operating specifications, material, accessibility, and cost. The table below outlines important criteria:
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Application | Performance requirements for process objectives |
Operating Specifications | Pressure and temperature ranges |
Material of Construction | Resistance to thermal stress |
Accessibility | Connections to utilities |
Space Constraints | System layout and floorplan limitations |
Housekeeping | Suitability for cleaning and maintenance |
Scalability | Ability to meet future needs |
Cost | Purchase, installation, and operating expenses |
Environment | Energy efficiency and carbon footprint |
A plate heat exchanger is often preferred for smaller approach temperatures and limited footprints. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger provides a hybrid solution, combining efficiency, durability, and expert support from Shanghai Heat Transfer for tailored applications.
Selecting the right heat exchanger depends on your process needs. The table below highlights key factors:
Type | Best For |
|---|---|
Plate heat exchanger | High efficiency, easy cleaning |
Shell and tube | Heavy-duty, high-pressure use |
Steam plate heat exchanger | Compact, energy-saving jobs |
Shanghai Heat Transfer offers expert support and advanced solutions for every application.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of a plate heat exchanger?
Plate heat exchangers provide high efficiency in a compact size. They are easy to clean and install. Many industries use them for energy savings.
How does the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger handle tough fluids?
The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from SHPHE uses welded corrugated plates. This design resists clogging and handles fluids with particles, fibers, or high viscosity.
Can I use a shell and tube heat exchanger for steam applications?
Yes. Shell and tube heat exchangers work well with steam. They handle high pressure and temperature. Many power plants and factories use them.





