Fully Welded Plate Heat Exchanger Solutions Trending in Chemicals
Chemical plants demand robust solutions for heat transfer. Fully Welded Plate Heat Exchanger technology now dominates due to its proven durability, leak-proof construction, and compact design.
Recent data shows the global heat exchanger market will reach USD 21.8 billion by 2030, driven by stricter regulations and the need for corrosion-resistant, energy-efficient equipment.
Key Demands in Chemical Industry Heat Exchange
1. Operational Complexity and Process Requirements
Chemical processing plants operate under strict process controls and face complex operational demands. Engineers use statistical process control tools, such as control charts and capability analysis, to monitor critical parameters. Regulatory agencies, including the FDA and EMA, require robust statistical validation and continuous process verification. Automated real-time monitoring and structured planning, supported by technology integration like AI, further address operational complexity.

SHPHE' Smart Eye digital monitoring system
2. Safety Challenge & Leak Prevention
Safety remains a top priority in chemical heat exchange. Leaks of toxic, flammable, or reactive fluids can cause severe environmental and safety hazards. Plants rely on conductivity and pH sensors, corrosion instruments, and safety instrumented systems for early leak detection. Regular visual inspections, pressure and temperature monitoring, and predictive maintenance tools help prevent unplanned shutdowns. Metallurgy selection and compliance with industry codes such as ASME, API, and TEMA ensure equipment integrity and regulatory adherence.
3. Efficiency, Maintenance, and Cost Pressures
High initial capital investments, ongoing maintenance expenses, and fluctuating raw material prices add to cost pressures, especially for small and medium enterprises. Reliable, durable equipment is crucial for maintaining efficiency and controlling costs in demanding chemical environments.
How Fully Welded Plate Heat Exchanger Solutions Impact Chemical Industry
A fully welded phe uses a series of corrugated metal plates, joined together by advanced welding methods such as laser or vacuum welding.
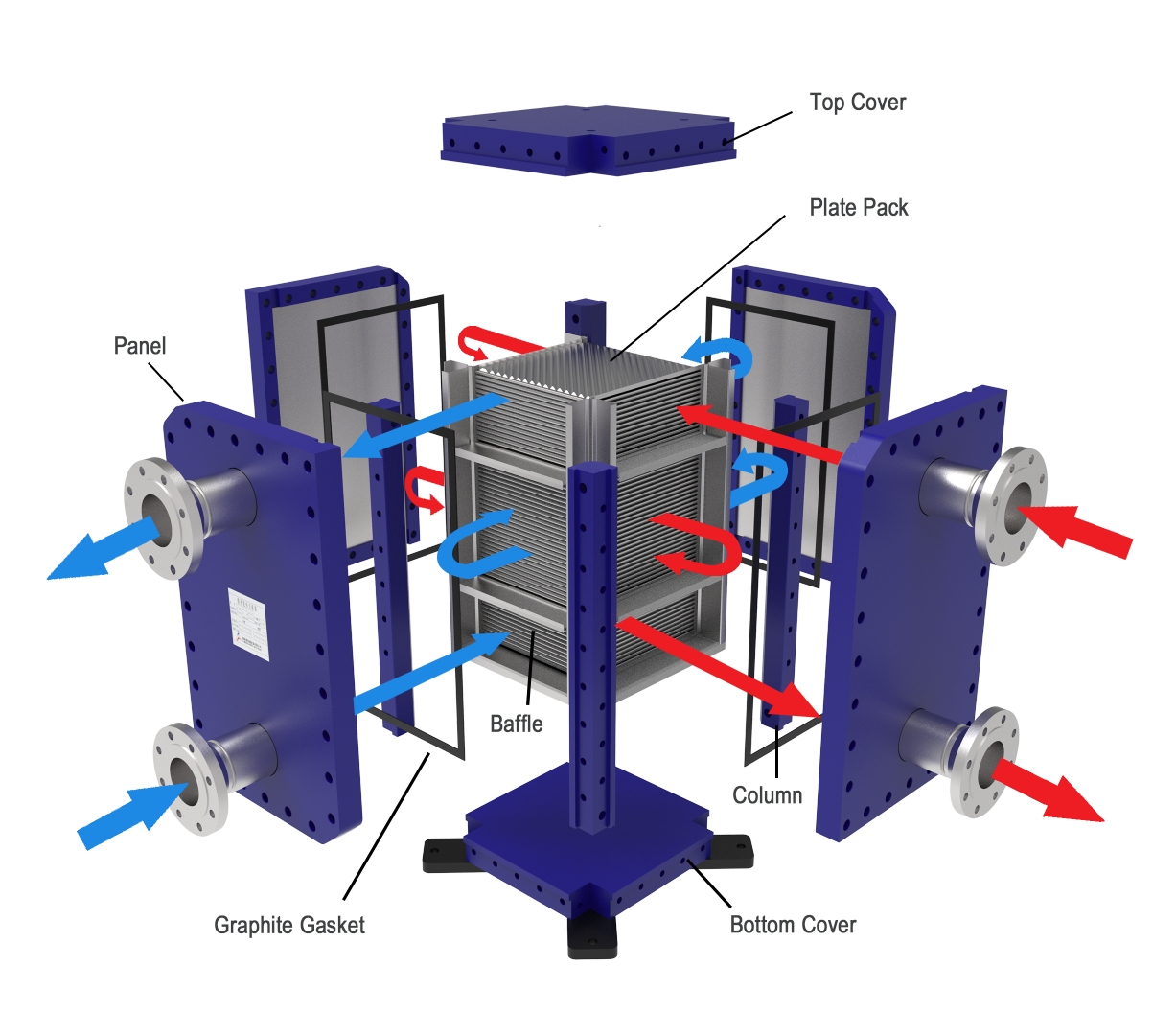
Fully welded designs offer:
· Enhanced safety by preventing leaks.
· Durability in corrosive and high-pressure environments.
· Reduced maintenance and downtime.
The welded construction eliminates the need for gaskets between plates, which removes the risk of leaks and increases reliability.
These laser welded plate heat exchangers can handle high pressures up to 50 barg and temperatures ranging from -50°C to 450°C. SHPHE use materials like stainless steel, titanium, and duplex alloys to ensure resistance to corrosion and mechanical stress.
The compact and modular structure allows for easy installation and maintenance, making these exchangers suitable for demanding chemical industry applications.

Benefits: Efficiency, Safety, and Cost Savings
Welded block heat exchanger deliver several advantages for chemical plants:
· Efficiency: The corrugated plate design creates turbulent flow, maximizing heat transfer and minimizing temperature differences. Plants achieve up to five times the efficiency of traditional shell and tube exchangers. The compact footprint saves valuable floor space.
· Safety: The welded construction eliminates gasket failure, reducing the risk of leaks and exposure to hazardous chemicals. This supports compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
· Cost Savings: Durable materials and robust design extend equipment life and reduce maintenance needs. Lower energy consumption and improved heat recovery translate to operational savings. Although initial investment may be higher, the long-term benefits outweigh the costs.
Innovations in Design, Materials, and Automation
Recent advancements have transformed the fully welded plate heat exchanger landscape. SHPHE now use patented structural features, such as soft corners, to improve mechanical strength and durability. The introduction of modular designs allows for easy access to the heat transfer area, simplifying cleaning and maintenance. Material innovations include the use of high-performance alloys like 254 SMO, C276, and titanium, which further boost corrosion resistance and lifespan.
Aspect | Details |
Design Innovation | Fully welded construction eliminates gaskets, ensuring leak-proof, maintenance-free operation. |
Application Suitability | Ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive fluid environments. |
Material Advancements | 304, 304L, 316L, 254SMO, C-276, Titanium |
Operational Benefits | Robustness and leak-proof nature improve safety and reliability. |
Market Trend | Growing adoption driven by energy efficiency and regulatory compliance. |
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Chemical plants use fully welded plate heat exchangers for heating, cooling, and heat recovery in a wide range of processes. For example, a biodiesel plant improved its product cooling system by installing a fully welded titanium plate heat exchanger. After cleaning with citric acid, the plant saw the heat transfer coefficient rise from 32.67 to 53.91 W/m²·K and the heat load double from 217,446 W to 434,984 W.
These results highlight the impact of proper maintenance and the exchanger’s ability to maintain high performance even in fouling-prone environments.
FAQs
What makes fully welded plate heat exchangers ideal for chemical plants?
Fully welded plate heat exchangers resist corrosion, prevent leaks, and handle high pressures. Their design ensures reliable performance in harsh chemical environments.
How often should operators perform maintenance on these exchangers?
Operators should follow manufacturer guidelines. Most fully welded designs require less frequent maintenance than gasketed models due to their robust construction.
Can fully welded plate heat exchangers handle aggressive chemicals?
Yes. Manufacturers use advanced alloys like titanium and C276. These materials withstand aggressive chemicals and extend equipment lifespan in demanding applications.
In what chemical plant situations are they most suitable?
Corrosive or toxic fluids (e.g., strong acids, solvents) and high-pressure, high-temperature systems.
Wide-gap welded designs are available for viscous fluids or those with particulates, reducing clogging risk.
How are fully welded plate heat exchangers cleaned and maintained?
Cleaning-in-place (CIP) is commonly used: circulating chemicals without disassembly.
Heavy fouling or blockages may require partial mechanical access or pressure flushing.
Operators should monitor temperature difference and pressure drop to detect fouling early.
What about cost and lifespan of welded heat exchanger in chemical plants?
Though capital cost is higher, FWPHEs generally offer lower lifecycle cost in harsh applications due to reduced maintenance and no gasket downtime.
Design life is typically 10 years, but with proper care can reach 20–40 years.
About SHPHE

SHPHE remains committed to driving industry progress through continuous technological innovation. By partnering with leading companies at home and abroad, SHPHE aims to become a top-tier provider of high-quality solutions in the heat exchange industry, both in China and internationally.
If you need further consultation and discussion, please feel free to contact us.
Email: info@shphe.com
WhatsApp /Cell: +86 15201818405




