How Plate Heat Exchangers Revolutionize Industrial Energy Use
Plate Heat Exchanger Fundamentals
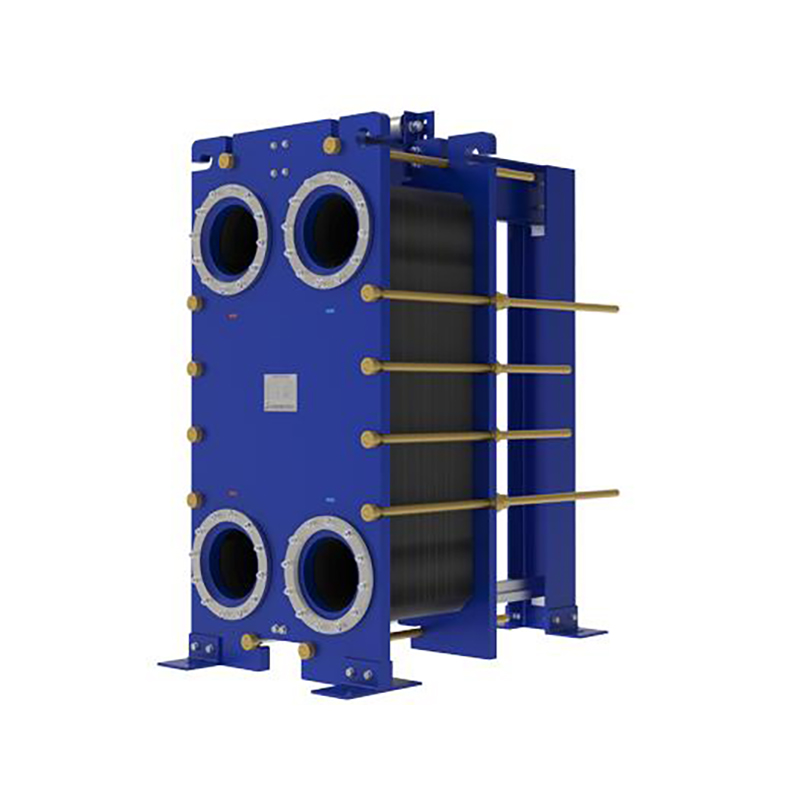

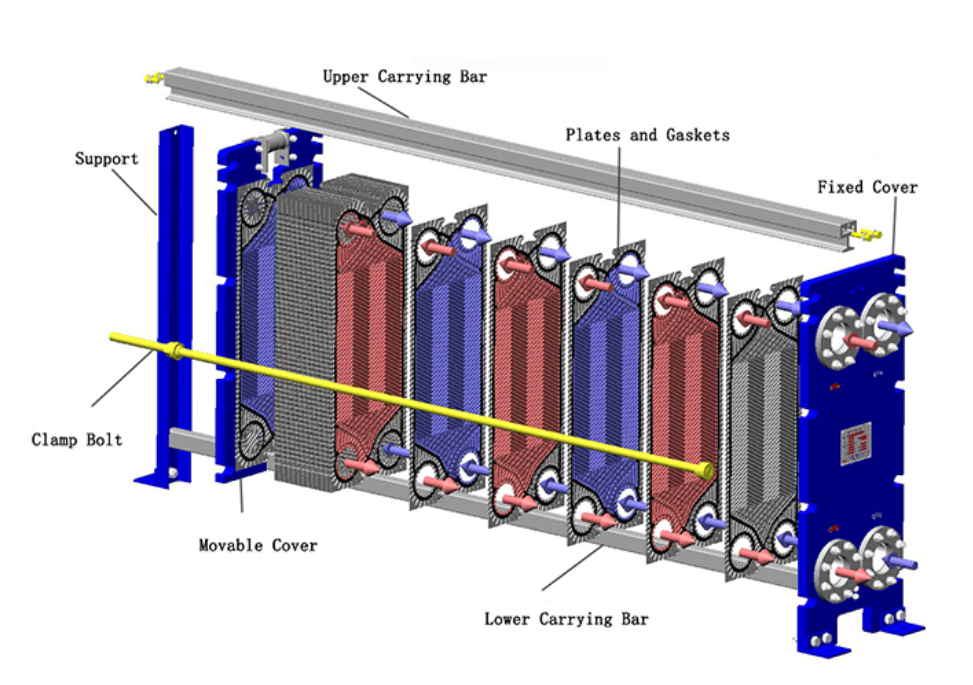
How Plate Heat Exchangers Work
A plate heat exchanger uses a series of thin, corrugated plates to transfer heat between two fluids. Each plate creates a channel for the fluids to flow. The fluids move in alternating channels, separated by the plates. Heat passes from the hot fluid to the cold fluid through the plate surface. This design increases the contact area, which boosts heat transfer efficiency.
Engineers value plate heat exchangers for their compact size and ability to handle high pressures. The modular structure allows easy expansion or maintenance. Operators can clean or replace plates without dismantling the entire unit.
Key Features and Design Advantages
Plate heat exchangers offer several advantages over traditional heat exchangers.
·High Efficiency: The large surface area of the plates maximizes heat transfer.
·Space Saving: The compact design fits into tight industrial spaces.
·Easy Maintenance: Plates can be removed and cleaned quickly.
·Flexible Operation: Units can adapt to different flow rates and temperatures.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Large surface area | Improved heat transfer |
| Modular design | Simple maintenance |
| Compact size | Space efficiency |
| Flexible setup | Versatile applications |
A plate heat exchanger supports energy recovery and reduces waste in many industries. Companies choose this technology to improve performance and lower costs.
Plate Heat Exchanger Benefits for Industrial Energy Use
Maximizing Energy Efficiency
Plate heat exchangers deliver outstanding energy efficiency in industrial environments. Their unique plate arrangement creates a large surface area for heat transfer. This design allows industries to recover more energy from process fluids. Operators can achieve higher thermal performance compared to traditional shell-and-tube exchangers.
Many facilities use plate heat exchangers to optimize energy use in heating and cooling systems. The close temperature approach between fluids reduces wasted energy. Engineers often select these units for processes that demand precise temperature control. As a result, companies see lower fuel consumption and improved overall system efficiency.
Reducing Operational Costs
Industrial leaders recognize the cost-saving potential of plate heat exchangers. The compact design minimizes installation expenses and frees up valuable floor space. Maintenance teams appreciate the ease of access to individual plates, which shortens downtime during cleaning or repairs.
A plate heat exchanger operates with lower pumping requirements due to its efficient flow paths. This feature reduces electricity costs for fluid circulation. Many organizations report significant savings on utility bills after switching to this technology.
| Cost Factor | Impact with Plate Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|
| Installation | Lower due to compact size |
| Maintenance | Reduced labor and downtime |
| Energy consumption | Decreased utility expenses |
| Equipment lifespan | Extended with proper care |
Supporting Sustainability and Environmental Goals
Plate heat exchangers play a vital role in advancing sustainability across industries. Their ability to recover and reuse energy helps companies reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Many organizations use these systems to meet strict environmental regulations and corporate responsibility targets.
Facilities that implement plate heat exchangers often experience less thermal pollution and lower water usage. The efficient heat transfer process minimizes waste and supports resource conservation. By choosing this technology, industries demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship.
Plate Heat Exchanger Applications and Industry Impact
Power Generation
Power plants rely on efficient heat transfer to maximize output and reduce fuel consumption. Engineers install plate heat exchangers to recover heat from steam and cooling water circuits. These units help maintain optimal temperatures in turbines and generators. Operators see improved energy recovery and lower emissions.
Chemical Processing
Chemical facilities demand precise temperature control for reactions and separations. Plate heat exchangers provide rapid heat exchange between process fluids. Technicians use them to cool, heat, or condense chemicals safely. The modular design allows quick adaptation to changing production needs.
Manufacturing and Food Processing
Manufacturers use plate heat exchangers to regulate temperatures in machinery and product lines. Food processors benefit from hygienic designs that support easy cleaning. These systems help maintain product quality and safety. Production teams achieve consistent results and reduce energy costs.
HVAC and Building Systems
Building managers choose plate heat exchangers for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. These units transfer heat between air and water circuits efficiently. Facility operators lower utility bills and improve indoor comfort. The compact size fits well in modern building layouts.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical companies require strict temperature control during drug production. Plate heat exchangers deliver reliable performance in sterile environments. Staff members appreciate the easy maintenance and flexibility. These systems support compliance with health and safety standards.
Innovation and Future Adaptability of Plate Heat Exchangers
Technological Advancements
Engineers continue to develop new features for plate heat exchangers. They use advanced materials such as stainless steel and titanium to improve durability and resistance to corrosion. Manufacturers design plates with enhanced patterns that boost heat transfer rates. Some companies introduce automated cleaning systems to reduce maintenance time.
Digital monitoring tools now track temperature and flow in real time. Operators use these systems to spot problems early and keep equipment running smoothly. Many facilities install sensors that send alerts when performance drops. These innovations help industries maintain high efficiency and reduce downtime.
Flexibility for Evolving Industrial Needs
Industries face new challenges as processes change and regulations tighten. Plate heat exchangers offer flexible solutions for these demands. Teams can add or remove plates to adjust capacity. This modular approach supports quick upgrades and easy repairs.
A plate heat exchanger fits into many different systems, from small-scale labs to large factories. Operators can customize units for specific fluids, temperatures, or pressures. This adaptability makes the technology valuable for both new installations and retrofits.
| Adaptability Feature | Benefit for Industry |
|---|---|
| Modular design | Fast expansion |
| Custom configurations | Precise temperature control |
| Wide material options | Compatibility with various fluids |
Industries rely on plate heat exchangers to meet future needs and stay competitive.
·Plate heat exchanger technology drives efficiency and cost savings in industrial operations.
·Industries rely on its adaptability to meet evolving energy demands.
·Companies that invest in this solution strengthen their competitive edge and support environmental responsibility.
FAQ
What maintenance do plate heat exchangers require?
Operators should inspect plates regularly, clean surfaces, and check for leaks. Scheduled maintenance extends equipment life and ensures optimal performance.
Can plate heat exchangers handle corrosive fluids?
Engineers select materials like titanium or stainless steel for corrosive fluids. These materials resist damage and maintain system reliability.
How do plate heat exchangers improve energy savings?
Plate heat exchangers recover waste heat efficiently. Facilities reduce fuel use and lower energy bills by maximizing heat transfer.





