How to Identify the Perfect Titanium Plate Heat Exchanger for Corrosive Environments
Selecting a titanium plate heat exchanger for corrosive environments requires careful attention to several factors. Experts recommend considering the corrosiveness of process fluids, operating conditions, raw material availability, and project budget. The HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger features advanced plate design and titanium construction, offering reliable performance in demanding applications.
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Corrosiveness of Process Fluids | High resistance to aggressive chemicals is essential. |
Operating Conditions | Temperature and pressure ratings must suit the environment. |
Availability of Raw Materials | Sourcing titanium affects lead time. |
Project Budget | Material choice impacts overall costs. |
Titanium Plate Heat Exchanger Selection Criteria

Titanium Grade and Alloy Choice
Selecting the right titanium grade is essential for maximizing corrosion resistance in a titanium plate heat exchanger. Titanium offers superior durability in harsh environments, such as chemical plants and seawater applications. Different grades provide unique benefits. The table below highlights the most commonly used grades and their properties:
Titanium Grade | Corrosion Resistance Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
Grade 1 | Excellent resistance to harsh chemicals | Chemical plants, heat exchangers |
Grade 2 | Good balance of strength and corrosion resistance | Versatile applications |
Grade 3 | High strength and excellent corrosion resistance | Strong, flexible applications |
Grade 4 | Strongest among commercially pure grades, good corrosion resistance | Tough applications |
Grade 5 | Strong, lightweight, and resistant to corrosion | Various applications |
Grade 7 | Improved resistance to crevice corrosion and acidic environments | Sulfuric and hydrochloric acid processing plants |
Titanium’s natural ability to resist corrosion ensures long-lasting durability. This advantage leads to extended equipment lifespan and lower energy losses, especially in environments with aggressive chemicals.
Plate Design and Thickness
Plate design and thickness play a critical role in heat exchanger selection. Engineers must consider the geometry and thickness of the plates to achieve high efficiency and optimal thermal transfer. Thicker plates increase mechanical strength and resistance to pressure, while advanced plate geometry enhances fluid dynamics. The HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger uses innovative plate designs to maximize heat transfer rates and minimize energy consumption. Facilities benefit from a compact footprint and modular construction, which allows for easy customization and scalability.
Gasket vs. Welded Construction
The choice between gasketed and welded construction impacts leak resistance and maintenance requirements. Welded heat exchangers, such as the HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger, provide very high leak resistance. This makes them suitable for toxic, flammable, or explosive media. Gasketed designs offer easier maintenance because users can disassemble the plates for cleaning or replacement. The table below compares these designs:
Design Type | Leak Resistance | Maintenance Requirements |
|---|---|---|
Gasketed | Relatively low (gaskets may fail under high temperature, pressure, or corrosion) | Easy (can be disassembled for mechanical cleaning) |
Welded | Very high (suitable for toxic, flammable, or explosive media) | Difficult (non-detachable plate pack, chemical cleaning only; shell side can be mechanically cleaned) |
Semi-Welded | Very high (creates a leak-tight barrier for one fluid) | More complex to maintain due to welded sections |
Welded titanium plate heat exchangers eliminate the risk of external leaks that can occur when gaskets degrade. They also provide superior resistance to pressure and temperature cycling, ensuring long-term reliability in demanding applications.
Gasket Material Compatibility
When selecting a gasketed plate heat exchanger, engineers must choose gasket materials compatible with titanium and the process fluids. The table below lists common gasket materials and their key properties:
Gasket Material | Key Properties |
|---|---|
NBR | Excellent resistance to oil, seawater, and mineral-based fluids. |
EPDM | Great heat, steam, and aging resistance, ideal for hot water applications. |
FKM | Outstanding chemical corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh acids and alkalis. |
Gasket material selection affects the overall performance and lifespan of the heat exchanger. For aggressive chemicals like hydrochloric acid or seawater, FKM and NBR gaskets offer the best compatibility.
Tip: Always match the gasket material to both the titanium plates and the process fluid to prevent premature failure and ensure high efficiency.
Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger’s HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger stands out as an advanced solution for corrosive environments. Its fully welded construction, modular design, and use of high-quality titanium deliver reliable, high efficiency performance and long-term durability.
Heat Exchanger Performance and Durability
Corrosion Resistance in Harsh Media
Corrosive environments challenge the durability of any heat exchanger. Titanium plate heat exchangers stand out because they resist damage from strong acids and chlorides. Many industries use them in chemical processing and seawater applications. The following table compares corrosion rates and service life for different materials:
Material | Corrosion Rate in Chloride Environments | Acid Resistance | Service Life |
|---|---|---|---|
GR7 Titanium Plate | <0.005 mm/year | Withstands 37% HCl and dilute sulfuric acid | Exceeds 15 years |
316 Stainless Steel | Susceptible to pitting corrosion | Perforates within 1 year in 15% HCl | 3-5 years |
Titanium plate heat exchangers provide a long service life and maintain high efficiency even in harsh conditions. Their resistance to corrosion reduces maintenance costs and downtime.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Industrial processes often require equipment that can handle high pressure and extreme temperatures. Titanium plate heat exchangers meet these demands. The HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger offers robust pressure and temperature ratings, making it suitable for many applications. The table below shows typical ratings:
Parameter | Rating |
|---|---|
Design Pressure | 0.6 – 4.0 MPa |
Design Temperature | -20℃ ~ 250℃ |
Titanium’s properties allow it to perform well in both hot and cold environments. The following table explains why titanium is a preferred choice for heat exchanger selection in corrosive applications:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Corrosion Resistance | Titanium exhibits extremely high corrosion resistance, especially in strongly acidic, strongly alkaline, and seawater environments. |
Application Suitability | Commonly used in seawater desalination, seawater cooling, and chemical processing due to its resistance to chloride corrosion. |
Alloy Enhancements | Titanium alloys can be engineered with elements like palladium or nickel to improve high-temperature resistance and mechanical strength. |
The HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger uses advanced titanium alloys to ensure reliable operation under demanding conditions.
Maintenance and Cleanability
Regular maintenance keeps heat exchangers running at peak performance. The HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger features a modular design and compact footprint, which makes cleaning easier. Users can access heat transfer channels for quick removal of deposits and scale. The table below lists common cleaning methods:
Cleaning Method | Description |
|---|---|
Mechanical Cleaning | Physically removes fouling using brushes, scrapers, or high-pressure water jets. |
Chemical Cleaning | Uses chemical agents like acids and alkalis to dissolve fouling substances. |
Online Cleaning | Allows cleaning while the heat exchanger is in operation, using self-cleaning mechanisms or cleaning agents injected into the fluid. |
Facilities benefit from reduced downtime and improved energy efficiency. The modular design of the HT-Bloc allows for easy customization and scalability, which supports long-term reliability.
Note: Regular cleaning and inspection help maintain heat transfer efficiency and extend the life of the heat exchanger.
Supplier Reputation and Certification
Choosing a reputable supplier ensures product quality and safety. Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger has years of experience in manufacturing high efficiency heat exchangers for corrosive environments. The company holds important certifications that guarantee product reliability. The table below highlights key certifications:
Certification | Importance |
|---|---|
ISO | Ensures quality management and consistency in titanium fabrication |
ASME | Guarantees adherence to safety and engineering standards |
Customer-specific | Meets unique requirements of specific industrial applications |
Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger’s commitment to quality and safety makes it a trusted partner for industrial clients. Their HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger meets strict standards and delivers reliable performance in challenging environments.
Heat Exchanger Selection Checklist
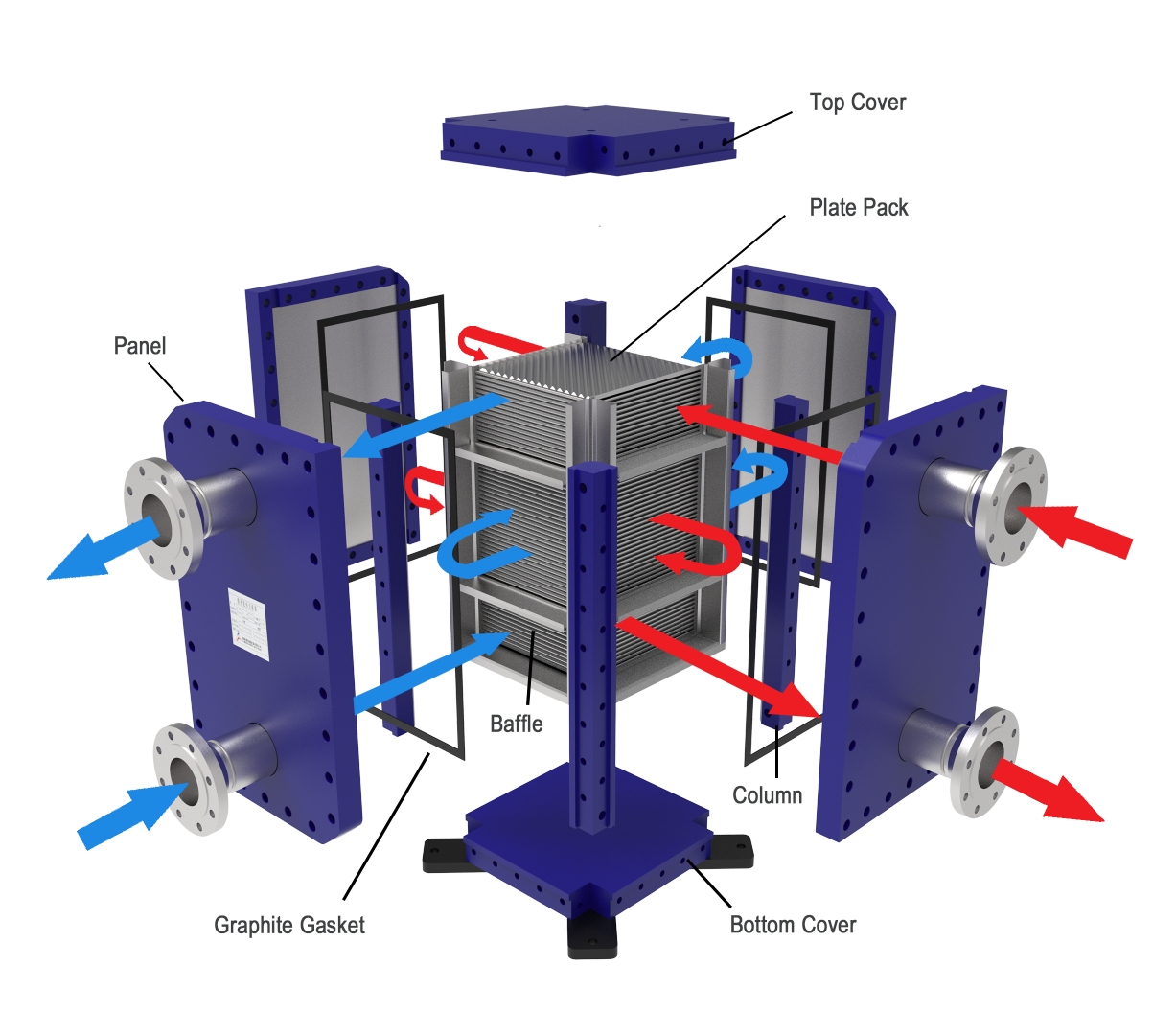
Step-by-Step Evaluation
Engineers and buyers can follow a clear process for heat exchanger selection in corrosive environments. The steps below help ensure the right choice for long-term reliability:
Material Selection: Titanium offers strong corrosion resistance. Specialized alloys can further enhance durability.
Surface Treatments: Techniques like anodizing or electroplating create protective barriers on the plates.
Operating Conditions Assessment: Evaluate temperature, pressure, and fluid type to match the heat exchanger to the environment.
Corrosion Monitoring: Regular inspections and corrosion sensors help maintain efficiency and prevent unexpected failures.
Tip: Modular designs, such as the HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger, allow easy customization and cleaning, which supports long-term performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
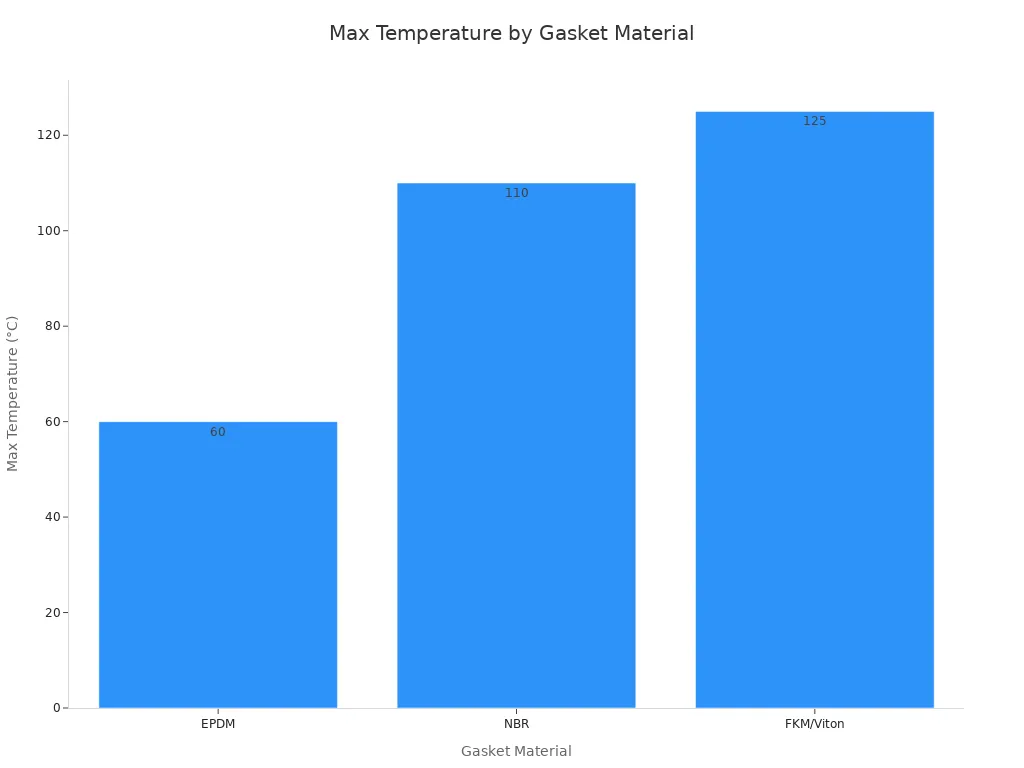
Selecting the wrong gasket or plate material can lead to early failure. The table below shows suitable gasket materials for different applications and temperature ranges:
Gasket Material | Suitable Applications | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
EPDM | Chlorinated water, ozone, dilute acids/alkalis | ~35–60 °C |
NBR | Oil or hydrocarbons | Up to ~110 °C |
FKM/Viton | Chemical-plant effluents containing acids | Up to ~125 °C |
Neoprene (CR) | Chlorinated or seawater coolers | N/A |
Buyers sometimes overlook the importance of matching plate alloys to the process fluid. Titanium plates work best in aggressive chemical processes. Stainless steel suits general applications, but titanium provides better longevity and reduces fouling in harsh conditions.
Note: Always review the operating environment and consult with experienced suppliers like Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger to avoid mismatches and ensure optimal heat exchanger performance.
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Superior Corrosion Resistance | Titanium resists corrosion, ensuring durability in harsh conditions. |
Optimal Heat Transfer Efficiency | Advanced plate design maximizes energy savings. |
Durability | Long service life reduces maintenance costs. |
Titanium plate heat exchangers support industrial and marine systems. Their long-term value offsets higher initial costs. Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger provides expert guidance and advanced solutions like the HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger, meeting the growing demand for efficient, sustainable technology.
FAQ
What makes titanium ideal for corrosive environments?
Titanium resists corrosion from acids, alkalis, and seawater. This property extends equipment life and reduces maintenance needs.
How does the HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchanger support easy cleaning?
The modular design allows users to access heat transfer channels. This feature simplifies cleaning and helps maintain high efficiency.
Does Shanghai Plate Heat Exchanger provide custom solutions?
Yes, the company offers customizable HT-Bloc Welded Plate Heat Exchangers. They adapt designs to meet specific industrial requirements.





