5 key roles of plate heat exchanger gaskets.
Plate heat exchanger gaskets perform 5 key roles: ...
More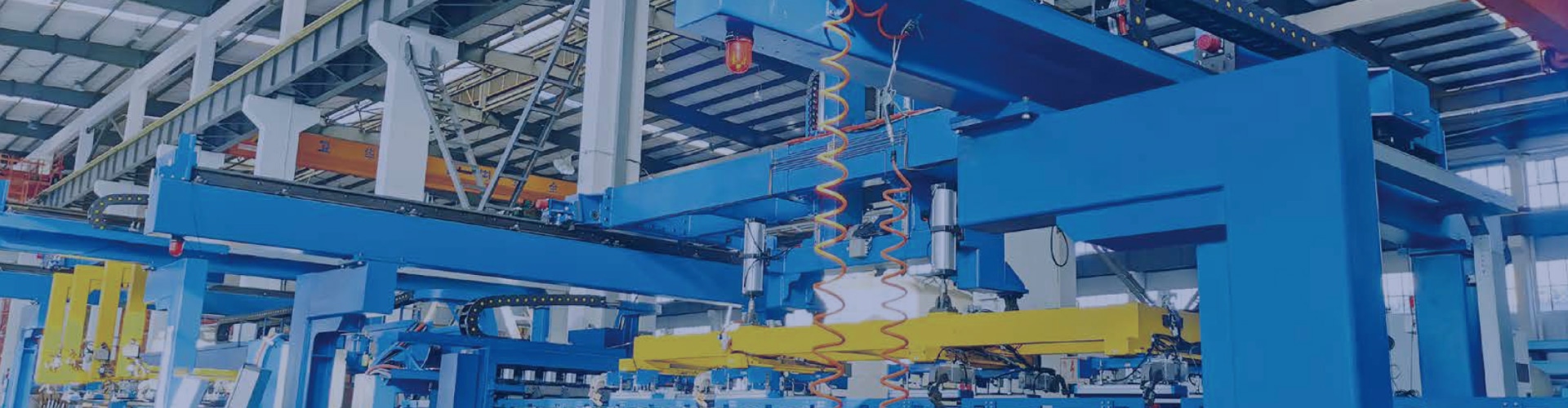
The fundamental principle of a plate to plate heat exchanger, also widely known as a plate heat exchanger (PHE), revolves around efficient thermal energy transfer between two fluids without mixing them. This is achieved through a design consisting of a series of corrugated metal plates compressed together within a frame, creating alternating channels for the hot and cold media. The highly efficient heat transfer is a direct result of the large surface area provided by the plates and the intense turbulence induced by their corrugated patterns, which disrupts laminar flow and minimizes thermal resistance. This design ensures that the fluids remain separated by the thin plates, which are typically made from stainless steel or other alloys resistant to corrosion, allowing conductive heat transfer to occur rapidly. The counter-current flow arrangement, where the two fluids run in opposite directions, maximizes the temperature difference between them across the entire length of the unit, leading to a very high thermal efficiency often exceeding 90% in most industrial applications. This efficient principle makes plate heat exchangers significantly more compact and effective than traditional shell and tube models for a wide range of duties, providing superior heat recovery and precise temperature control.
The operational principle of a plate heat exchanger is engineered for maximum efficiency. The corrugations on each plate are not random; they are precisely designed to enhance fluid turbulence, which drastically improves the heat transfer coefficient. This high turbulence also helps in reducing fouling, as it minimizes the chances of particles settling on the heat transfer surfaces. Gaskets, typically made from elastomers like NBR or EPDM, are placed between the plates to seal the channels and direct the fluids into their respective alternate passages, preventing any cross-contamination. The entire pack of plates is clamped between a fixed frame plate and a movable pressure plate, allowing for easy opening for maintenance, cleaning, or capacity expansion by adding or removing plates. This modularity is a key advantage, enabling the same frame to handle different thermal duties simply by adjusting the number of plates. The compact design, often resulting in a footprint up to 80% smaller than a equivalent shell and tube heat exchanger, is a direct benefit of this efficient principle, saving significant space in plant layout. This design is so effective that it can approach temperature approaches as low as 1°C, meaning the outgoing cold fluid can be heated to within a single degree of the incoming hot fluid's temperature, maximizing energy recovery.
Select the most popular foreign trade service products to meet your diverse needs
Learn more about the dynamics and professional knowledge of the foreign trade industry
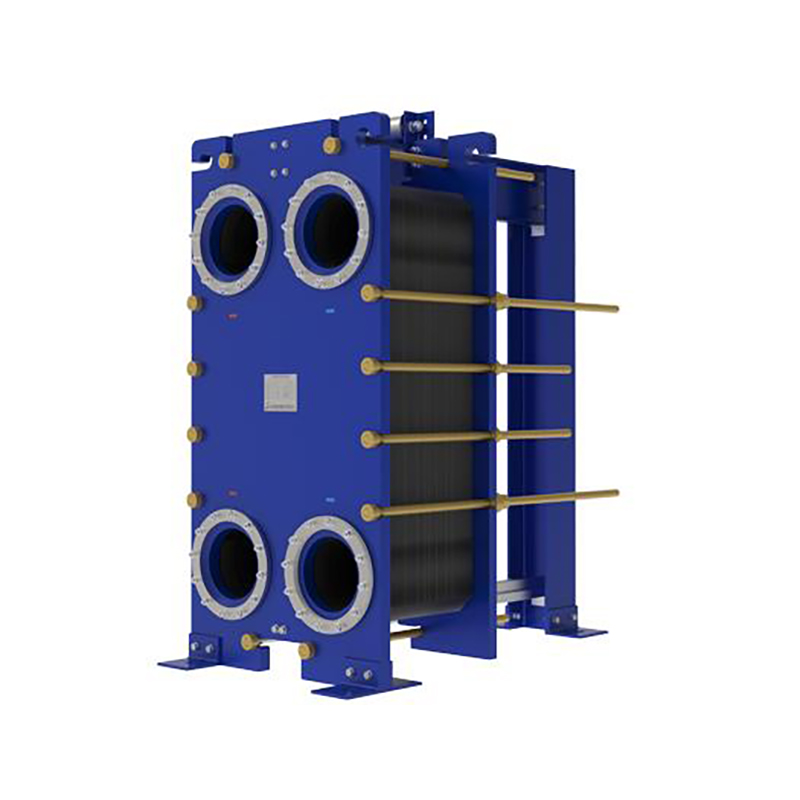

Plate heat exchanger gaskets perform 5 key roles: ...
More
Compare top frame plate heat exchanger models for ...
More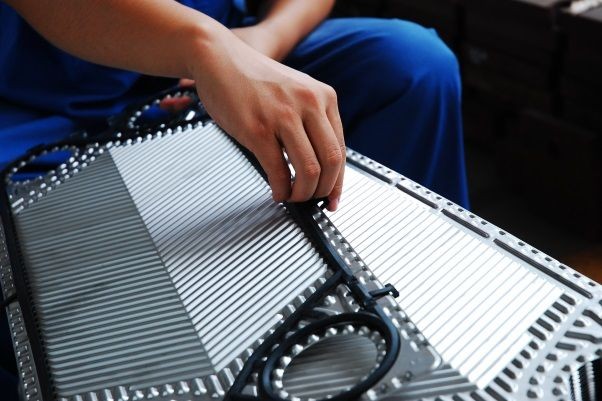
API 662 defines standards for plate heat exchanger...
More
You can see clear differences between welded block...
More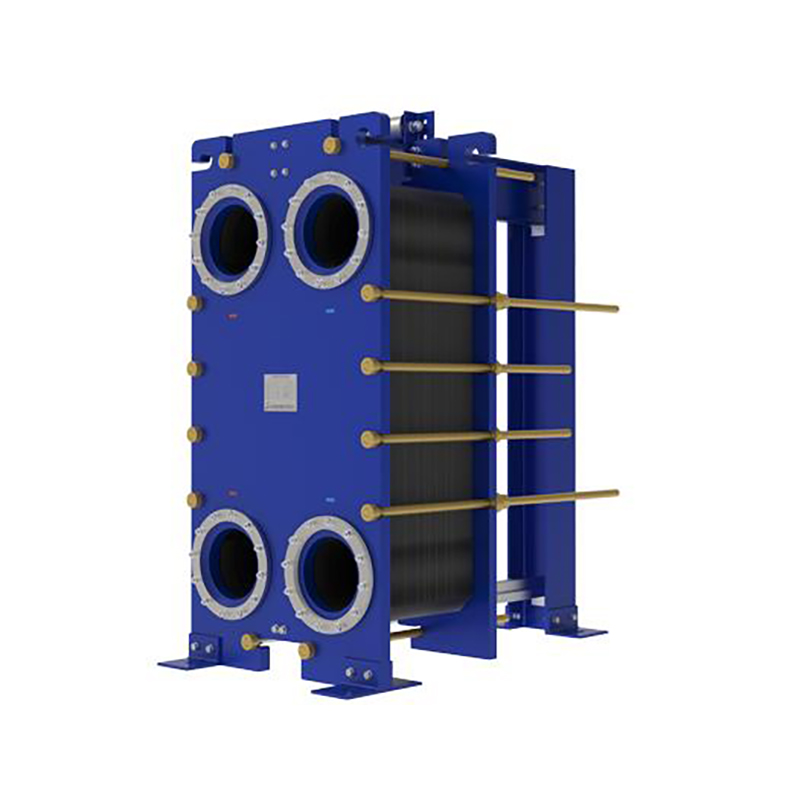
Shanghai Heat Transfer stands out with its ISO9001...
More
The dimple plate heat exchanger, also known as the...
MoreSelect the most popular foreign trade service products to meet your diverse needs
Explore more content related to foreign trade services

User Comments
Service Experience Sharing from Real Customers
David Chen
Maintenance EngineerThe plate design is incredibly efficient. We've seen a 30% improvement in heat transfer compared to our old shell and tube unit. Maintenance is also a breeze with the easy-to-clean plates.
Sarah Wilkinson
Plant ManagerExceptional build quality and performance. This exchanger has been running flawlessly for over a year in our dairy plant, handling pasteurization duties with perfect temperature control and no issues.
Michael Rodriguez
HVAC Project LeadA very compact and space-saving solution for our district heating system. Installation was straightforward, and it's performing exactly as specified. Took one star off for the initial lead time being a bit long.
Emily Foster
Process TechnicianThe flexibility to add or remove plates to adjust capacity is a game-changer for our R&D pilot plant. It allows us to perfectly scale the heat exchanger for different processes and batches.