5 key roles of plate heat exchanger gaskets.
Plate heat exchanger gaskets perform 5 key roles: ...
More
A plate type heat exchanger operates on the principle of transferring heat between two fluids without mixing them, using a series of corrugated metal plates stacked together. These plates create alternating channels for the hot and cold fluids to flow through, facilitating efficient thermal exchange. The corrugations on the plates enhance turbulence, which significantly improves heat transfer rates compared to traditional shell-and-tube designs. Gaskets or laser welding seal the plates, ensuring the fluids remain separate while optimizing pressure distribution. This compact and modular design allows for high heat recovery, making it ideal for applications requiring precise temperature control, such as HVAC systems, industrial processing, and refrigeration. The efficiency of plate heat exchangers often exceeds 90% in many scenarios, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
Plate type heat exchangers are engineered for maximum thermal efficiency, leveraging advanced plate geometries to achieve heat transfer coefficients that can range from 3,000 to 7,000 W/m²K, depending on the fluid properties and flow conditions. The plates, typically made from stainless steel or titanium, are pressed with patterns like herringbone or chevron to create turbulent flow even at low velocities, which minimizes fouling and maximizes surface area contact. For instance, in dairy pasteurization, these exchangers can heat or cool products rapidly, with approach temperatures as low as 1-2°C, ensuring energy savings of up to 40% over conventional systems. The flexibility in plate arrangement allows for customization of performance: by adjusting the number of plates or their angles, engineers can tailor the exchanger to handle specific duties, such as high-viscosity fluids or high-pressure environments up to 25 bar. This adaptability, combined with a compact footprint—often 50% smaller than shell-and-tube units—makes them a preferred choice for industries aiming to optimize space and reduce capital costs while maintaining high operational reliability.
Select the most popular foreign trade service products to meet your diverse needs
Learn more about the dynamics and professional knowledge of the foreign trade industry
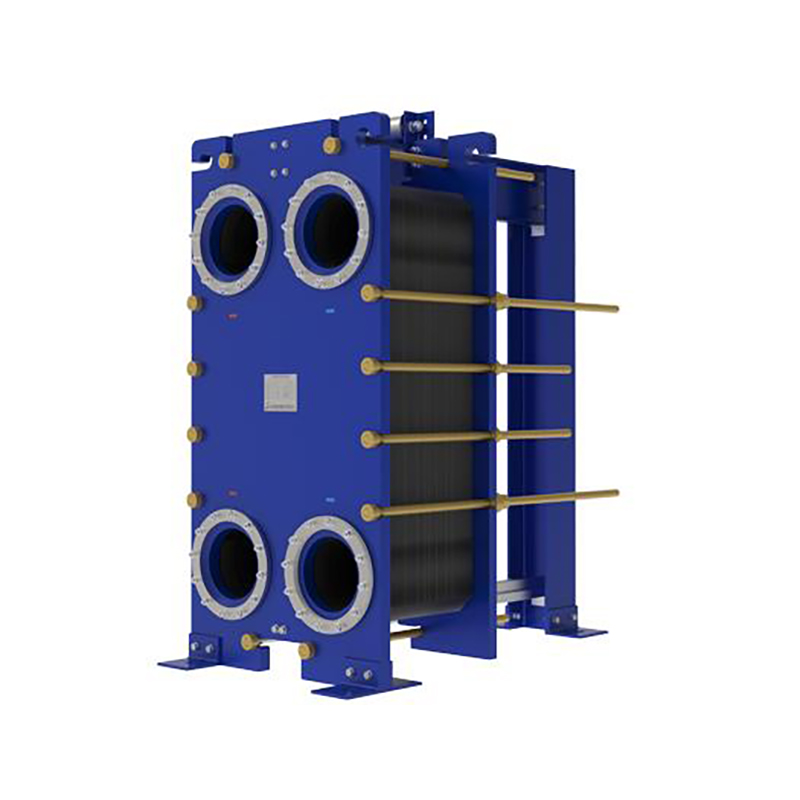

Plate heat exchanger gaskets perform 5 key roles: ...
More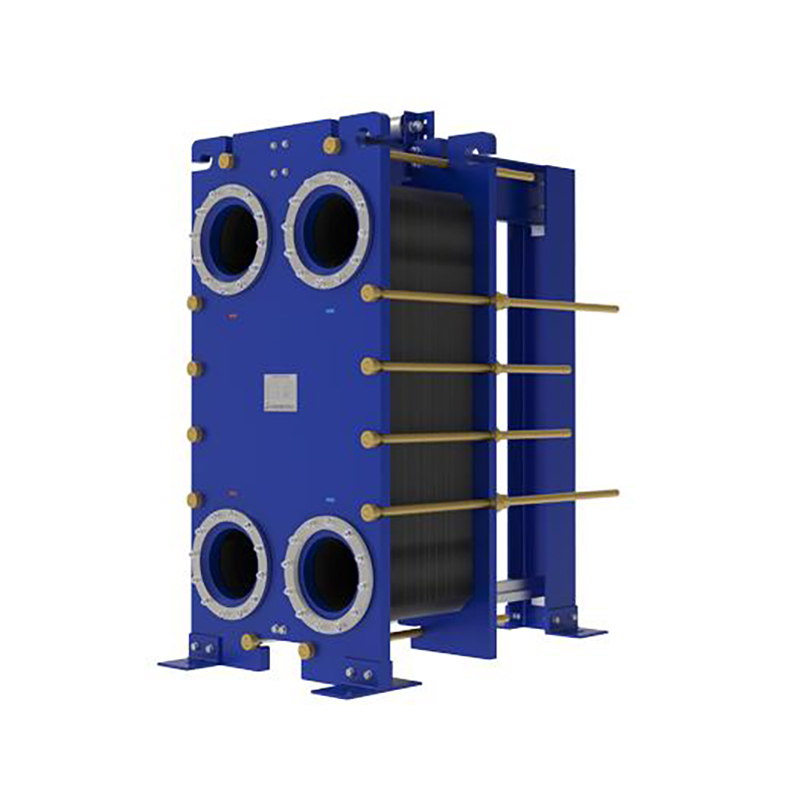
A gasket in heat exchanger seals surfaces, blocks ...
More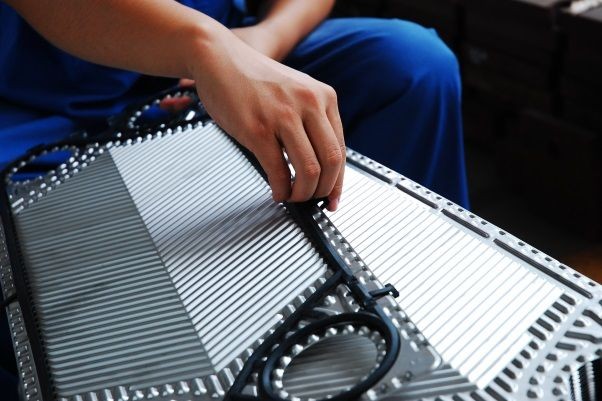
API 662 defines standards for plate heat exchanger...
More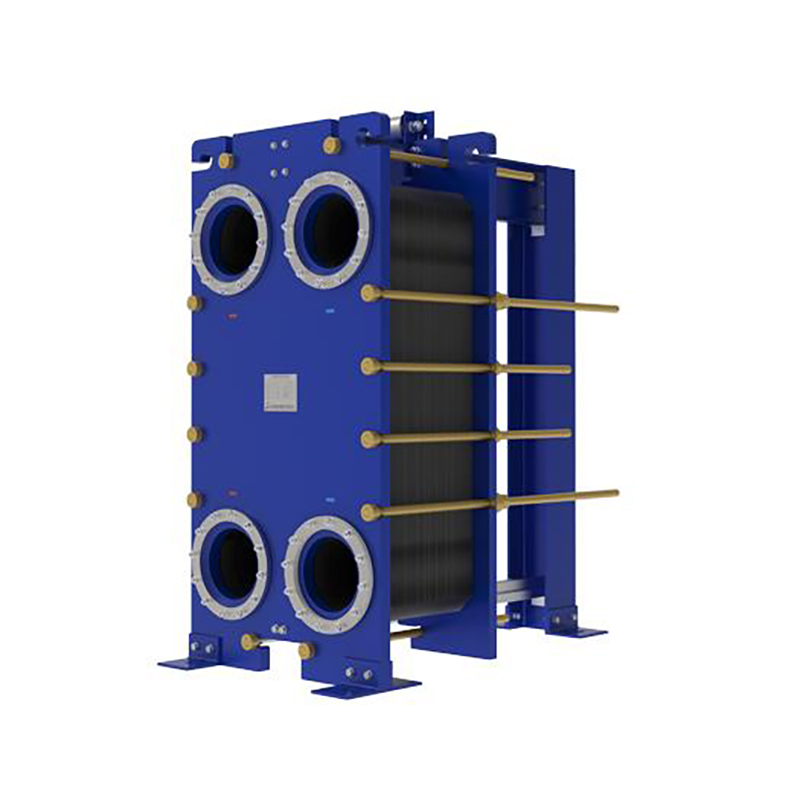
Compare top frame plate heat exchanger models for ...
More
You can see clear differences between welded block...
More
The dimple plate heat exchanger, also known as the...
MoreSelect the most popular foreign trade service products to meet your diverse needs
Explore more content related to foreign trade services

User Comments
Service Experience Sharing from Real Customers
Michael Chen
Maintenance EngineerThis plate heat exchanger is incredibly efficient and robust. The compact design saved us significant space, and the heat transfer performance exceeded our expectations. Maintenance is also straightforward. Highly recommended for industrial applications.
Sarah Johnson
Plant ManagerWe installed this unit in our dairy processing line six months ago. It's been flawless. The sanitation is excellent, and it handles our high-capacity pasteurization needs perfectly. A reliable and high-performing piece of equipment.
David Williams
HVAC Project LeadA great solution for our district heating system. The thermal efficiency is top-notch, leading to noticeable energy savings. The only reason it's not a 5 is that the initial gasket configuration was slightly complex, but the supplier support was excellent.
Lisa Rodriguez
Chief EngineerAs a marine chief engineer, I need equipment I can depend on. This plate exchanger has been vital for our central cooling system aboard the vessel. It's durable, corrosion-resistant, and performs consistently even under demanding conditions at sea.