The Complete Guide to Welded PHE Selection for Industrial Use
The Complete Guide to Welded PHE Selection for Industrial Use

Selecting the right welded PHE plays a crucial role in industrial heat exchangers. The process starts with understanding key requirements that impact both performance and efficiency. These include operating temperature and pressure ranges, chemical properties of the fluids, required flow rates, and necessary heat transfer capacity. Advanced heat exchanger solutions like the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer offer reliable and durable options for demanding applications. Their innovative solutions help industries achieve high efficiency and long-term reliability.
Welded PHEs in Industrial Heat Exchangers
What Is a Welded PHE?
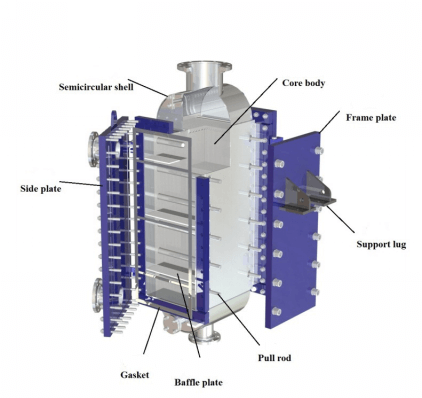
A welded PHE, or welded plate heat exchanger, uses a series of metal plates joined together by welding. This construction creates strong, leak-resistant channels for fluids. Unlike gasketed models, welded plate heat exchangers do not rely on gaskets, which reduces the risk of leaks and allows operation under higher pressures and temperatures. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer features a hybrid design that combines the compactness and high efficiency of plate heat exchangers with the durability of shell and tube models. Its openable structure allows easy access for cleaning and maintenance. Material options include stainless steel, titanium, and Hastelloy, which provide excellent corrosion resistance.
Characteristic | Welded Plate Heat Exchangers | Other Heat Exchanger Types |
|---|---|---|
Construction | Fully welded circular plate pack | Various constructions (e.g., shell and tube) |
Efficiency | High heat transfer efficiency | Varies by type |
Application Suitability | Suitable for high pressure and temperature applications | Varies by type |
Leakage Prevention | No gaskets, reducing risk of leakage | Often uses gaskets |
Size | Compact size | Varies by type |
Fouling | Low fouling potential | Varies by type |
Temperature Approach | Close approach temperature | Varies by type |
Key Benefits for Industrial Use
Welded plate heat exchangers offer several advantages for industrial heat exchangers. They deliver high performance and efficiency, which helps industries save energy and reduce costs. These units can boost productivity by reducing unplanned downtime by up to 70%. Advanced cooling technology achieves up to 30% energy savings. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger supports cleaning-in-place systems, making maintenance simple and fast. Its design handles challenging fluids, including viscous and particle-laden substances, which increases reliability in industrial applications.
Tip: Welded plate heat exchangers work well in demanding environments, such as hydraulic presses and food processing plants.
When to Choose Welded Over Gasketed
Industries select welded plate heat exchangers when processes require high pressure, extreme temperatures, or when fluids are aggressive or hazardous. Welded PHEs suit applications where gasketed models may fail due to leakage risks or chemical compatibility issues. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer fits a wide range of applications, including liquid-liquid, gas-gas, and liquid-gas processes. Major sectors using welded plate heat exchangers include:
Oil & Gas
Chemical Processing
Power Generation
Food & Beverage
Pharmaceuticals
HVAC & Refrigeration
These sectors rely on welded plate heat exchangers for their compact size, low fouling potential, and ability to handle multiple streams. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger stands out for its versatility and robust performance in industrial heat exchangers.
Temperature and Pressure Requirements
Industrial heat exchangers must handle a wide range of temperatures and pressures. The operating limits of a welded phe depend on the process and the selected materials. The following table shows typical ranges for welded plate heat exchangers used in industrial settings:
Source | Max Pressure (bar) | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|
JAQS | 100 | N/A |
Tranter (SUPERMAX) | 100 | -195 to 900 |
Tranter (NovusBloc) | 42 | -50 to 375 |
The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer operates reliably from -196°C up to 900°C and can withstand pressures up to 60 bar. These capabilities make it suitable for demanding applications such as oil and gas, metallurgy, and food processing. Matching the plate heat exchanger to the process temperature and pressure ensures safe operation and consistent performance.
Tip: Always verify that the selected plate heat exchanger meets or exceeds the maximum expected temperature and pressure for your application.
Flow Rate and Sizing Considerations
Flow rate and sizing play a major role in the performance of industrial heat exchangers. The correct size and capacity ensure efficient heat transfer and prevent issues like excessive pressure drop or insufficient cooling. Engineers must calculate the required flow rates for both hot and cold streams. They also need to consider the physical size of the unit to fit available space.
Key factors for sizing include:
Required heat transfer rate (capacity)
Flow rates of process fluids
Allowable pressure drop
Space limitations in the facility
A properly sized plate heat exchanger maximizes efficiency and reduces energy costs. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger offers a compact design, making it easy to install in tight spaces while delivering high performance. This flexibility supports a wide range of applications, from small-scale operations to large industrial processes.
Callout: Accurate flow rate and sizing calculations lead to better performance, lower maintenance costs, and longer equipment life.
By carefully defining process needs—fluid properties, temperature and pressure requirements, and flow rate—engineers can select the best plate heat exchanger for any industrial application. This approach ensures reliable performance and optimal efficiency for every project.
Material Selection and Corrosion Resistance
Material Options for Welded PHEs
Engineers select heat exchanger materials based on the demands of industrial applications. Each material offers unique properties that affect performance, durability, and efficiency. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer uses advanced heat exchanger materials to deliver reliable results in industrial heat exchangers. The following table shows common choices and their applications:
Material | Properties and Applications |
|---|---|
Stainless Steel (304, 316) | Corrosion resistance and mechanical strength; suitable for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. |
Titanium | Exceptional resistance to chlorides and seawater; ideal for coastal facilities and chemical processing. |
Nickel Alloys (Hastelloy, Inconel) | Preferred in high-temperature, highly corrosive environments like chemical reactors and power plants. |
Graphite | Resistance to strong acids and high purity; used in pharmaceuticals and specialty chemical manufacturing. |
Copper and Copper Alloys | High thermal conductivity; chosen for HVAC and refrigeration systems with non-corrosive fluids. |
Aluminum | Lightweight and highly conductive; common in air-cooled heat exchangers for energy efficiency. |
Selecting the right heat exchanger materials improves performance and extends equipment life. Stainless steel and titanium remain popular for their balance of strength and corrosion resistance. Nickel alloys provide extra protection in harsh environments.
Corrosive Media and Compliance
Industrial heat exchangers often face corrosive fluids. The choice of heat exchanger materials determines how well a plate heat exchanger resists damage and maintains efficiency. The table below highlights how different materials perform in corrosive media:
Material Type | Corrosion Resistance Characteristics | Application Considerations |
|---|---|---|
Stainless Steel Grades | Good resistance, suitable for many applications, but may require passivation in aggressive media. | Ideal for moderate corrosive environments, often used in food and chemical processing. |
Nickel-Based Alloys | Excellent resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, suitable for harsh conditions. | Best for high-temperature and high-pressure applications where corrosion is a concern. |
Titanium | Outstanding resistance to a wide range of corrosive media, lightweight and strong. | Used in highly corrosive environments, such as seawater and chemical processing. |
Surface Treatments | Techniques like anodizing and electroplating enhance base material resistance. | Important for extending the lifespan of heat exchangers in corrosive applications. |
Corrosion Inhibitors | Chemical additives that form protective layers, reducing reactivity with corrosive elements. | Effective in prolonging the life of heat exchangers in challenging environments. |
Shanghai Heat Transfer uses heat exchanger materials that meet strict industry standards. Their TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger supports titanium plates and FKM gaskets for saltwater resistance. Surface treatments and corrosion inhibitors further improve performance in demanding applications.
Tip: Choosing the right heat exchanger materials for corrosive media ensures long-term efficiency and safety in industrial applications.
Shanghai Heat Transfer’s Expertise
Shanghai Heat Transfer demonstrates expertise in selecting and applying heat exchanger materials for industrial heat exchangers. Their TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger meets international standards for quality and corrosion resistance. The company holds certifications that prove their commitment to performance and reliability:
Certification/Compliance | Description |
|---|---|
ISO 9001 | Quality management system certification |
CE | Compliance with European safety standards |
CCS | Certified by China Classification Society for marine applications |
Titanium plates (TA1 Grade) provide enhanced corrosion resistance.
FKM gaskets withstand saltwater corrosion.
Products show durability in harsh marine environments.
Shanghai Heat Transfer’s engineering team helps clients select the best heat exchanger materials for each application. Their expertise ensures that every plate heat exchanger delivers high performance, efficiency, and safety in industrial applications.
Design Features and Performance Factors
Plate Geometry and Channel Design
Plate geometry plays a vital role in the performance of welded plate heat exchangers. Engineers at Shanghai Heat Transfer use advanced heat exchanger materials and design patterns to maximize efficiency. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger features corrugated plates with different angles. Steep corrugation angles, known as thermal long patterns, increase turbulence and boost heat transfer. Shallow angles, called thermal short patterns, reduce turbulence and lower pressure drop. Mixed patterns balance heat transfer and pressure drop for various applications. Computational fluid dynamics studies show that geometry affects flow behavior and heat transfer efficiency. Optimized channel design leads to high performance in industrial heat exchangers.
Thermal long pattern: High turbulence, high heat transfer, higher pressure drop.
Thermal short pattern: Lower turbulence, moderate heat transfer, lower pressure drop.
Thermal mix pattern: Balanced performance for changing conditions.
Openable Structure and Maintenance
The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger stands out for its openable structure. This design allows easy access to all four sides, making maintenance and cleaning routines simple. Operators can inspect and clean the unit without removing it from service. The openable structure reduces downtime and supports operational and maintenance factors in industrial applications. Regular maintenance prevents fouling and scaling, which can lower efficiency and performance.
Performance Optimization
Performance optimization strategies improve the effectiveness of welded plate heat exchangers. Engineers focus on flow uniformity and geometrical parameters. Studies show that optimizing plate thickness and channel design increases thermal effectiveness by 13% and heat transfer rate by 30.49%. Pressure drop can decrease by up to 56.9%. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger uses advanced heat exchanger materials and design and sizing techniques to achieve these results. Performance optimization ensures reliable operation in industrial applications and supports long-term efficiency.
Callout: Optimized design and sizing, along with proper heat exchanger materials, lead to better performance and lower maintenance costs.
Efficiency, Cost, and Lifecycle Performance
Thermal Efficiency and Pressure Drop
Thermal efficiency stands as a key factor in the performance of industrial heat exchangers. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer uses advanced heat exchanger materials and a compact design to maximize process efficiency. Pressure drop values play a major role in system efficiency.
Higher pressure drop increases energy consumption for pumping fluids, which raises operational costs.
Optimizing pressure drop improves heat transfer efficiency and reduces energy use.
Maintaining flow in the turbulent regime enhances heat transfer, which is crucial for overall system efficiency.
Engineers select heat exchanger materials and plate geometry to balance pressure drop and heat transfer. This approach ensures high performance in demanding applications.
Maintenance and Operating Costs
Maintenance practices affect both performance and cost in industrial applications. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger supports easy access for cleaning and inspection, which helps reduce downtime. The table below outlines typical maintenance tasks for welded plate heat exchangers:
Maintenance Practice | Description |
|---|---|
Regular Inspections | Inspect for corrosion, erosion, or physical damage to maintain efficiency. |
Daily Cleaning | Remove dust and contaminants to ensure optimal heat transfer. |
Check for leaks | Inspect joints and welds to prevent leaks and maintain integrity. |
Tighten connections | Regularly check and tighten connections to minimize leaks. |
Choose repairable designs | Opt for modular designs that allow for easy maintenance and lower long-term costs. |
Proactive inspections | Use advanced testing methods to detect issues early, preventing costly downtime. |
Leverage energy efficiency | Invest in high-efficiency models to reduce long-term energy costs and improve sustainability. |
Selecting the right heat exchanger materials reduces the frequency of repairs and extends equipment life. Proper maintenance ensures consistent performance in a wide range of applications.
Shanghai Heat Transfer uses high-quality heat exchanger materials to ensure durability and reduce replacement costs. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger delivers reliable performance in industrial heat exchangers, making it a smart choice for many applications. By focusing on process efficiency, energy efficiency, and the right heat exchanger materials, companies can achieve lower total cost and better long-term results.
Compliance and Safety in Advanced Heat Exchanger Solutions
Industry Standards and Certifications
Industrial facilities must follow strict compliance rules when selecting welded plate heat exchangers. Regulatory bodies set standards to ensure safety, reliability, and performance. Shanghai Heat Transfer designs the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger to meet these requirements. The company uses heat exchanger materials that pass rigorous tests and inspections. The following table lists important certifications and standards for regulatory compliance:
Certification Standard | Description |
|---|---|
ASME | Section VIII, Division 1 |
TEMA | Classes B, C, R |
3-A | Sanitary Standards |
ASME Code "U" Stamp | Certification for pressure vessels |
National Board Registration | Registration for pressure vessels |
ISO 9001 | Quality Management Certification |
ASME BPE | Bioprocessing Equipment Compliance |
Hydrostatic Pressure Testing | Certification for pressure testing |
Dye Penetrant Testing | Certification for weld integrity |
Passivation Certification | Certification for corrosion resistance |
Profilometer Surface Finish Certification | Certification for surface finish quality |
Thermal Performance Validation | Validation of thermal efficiency |
Vibration and Resonance Testing | Testing for mechanical stability |
Radiographic (X-Ray) Inspection | Inspection for internal defects |
Comprehensive Documentation Package | Documentation for compliance |
Fiber Optic Borescope Inspection | Inspection for internal cleanliness |
Electropolishing Certification | Certification for surface treatment |
Facilities must check that their equipment meets these standards to maintain regulatory compliance. These certifications help prevent accidents and ensure long-term reliability.
Note: Regular audits and inspections help companies maintain compliance and avoid regulatory penalties.
Safety Features in Welded PHEs
Welded plate heat exchangers offer several safety features for industrial use. Their welded construction reduces the risk of leaks, which is important for high-pressure and high-temperature operations. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from Shanghai Heat Transfer does not use gaskets, so it avoids problems with gasket wear and degradation. This design improves safety and reliability. Operators can trust welded plate heat exchangers to protect workers and equipment in demanding environments. Regulatory agencies require these safety features to meet compliance standards.
Facilities often choose welded plate heat exchangers for their ability to handle hazardous fluids and extreme conditions. The use of high-quality heat exchanger materials also supports compliance with safety regulations. Regular maintenance and inspections further enhance safety and help companies meet regulatory requirements.
Tip: Always verify that your heat exchanger meets all regulatory compliance standards before installation.
Supplier Comparison and Custom Solutions
Evaluating Industrial Heat Exchanger Suppliers
Selecting the right supplier for industrial heat exchangers requires careful evaluation. Companies look at several criteria to make informed decisions. These criteria include operating conditions, fluid characteristics, space limits, efficiency, and compliance. Suppliers must provide products that meet regulatory standards and deliver reliable performance in various applications.
Key factors for supplier selection include:
Product efficiency
Material durability
Customization options
Compliance and certifications
Pricing and total cost of ownership
After-sales support and service
Innovation and R&D investment
Delivery and lead times
These factors impact the overall performance and cost-effectiveness of heat exchanger solutions. SCompanies must also consider how well suppliers support regulatory requirements and provide solutions that fit specific needs.
Tip: Strong after-sales service and technical support ensure long-term reliability and help maintain compliance with changing regulatory standards.
Customization and Support from Shanghai Heat Transfer
Shanghai Heat Transfer stands out in the market for its engineering expertise and customer focus. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger offers advanced solutions for industrial heat exchangers. The company works closely with clients to deliver custom solutions that meet unique process requirements and regulatory compliance.
The table below compares Shanghai Heat Transfer’s offerings with those of other suppliers:
Feature | Shanghai Heat Transfer (TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger) | Competitors (General) |
|---|---|---|
Global Standards and Certifications | Certified by ASME, NB, CE, ISO9001, ISO14001, OHSAS18001 | Varies, often less comprehensive |
Custom Design Capabilities | Full technical support and tailored solutions | Limited customization options |
Experience and Innovation | 18+ years, 30+ patents, advanced technologies | Less experience |
Global Reach | Exports to 20+ countries, responsive service | Limited international presence |
Shanghai Heat Transfer’s team provides technical support throughout the product lifecycle. They help clients achieve regulatory compliance and adapt to new standards. Their commitment to innovation and customer service ensures that each solution fits the client’s needs and meets all regulatory requirements.
Practical Tips and Selection Checklist
Key Selection Tips
Selecting a welded phe for industrial applications requires careful attention to several factors. Engineers should match materials to the operating environment. Stainless steel and titanium alloys work best in high-temperature and high-pressure settings. These materials offer strong thermal conductivity and durability, which improves performance. In corrosive environments, titanium, titanium alloys, or Hastelloy provide reliable solutions. For projects with budget limits, stainless steel with corrosion-resistant coatings can balance cost and efficiency. Carbon steel and aluminum alloys suit less demanding applications, such as automotive radiators, where corrosion resistance is not critical. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from heattransfer delivers solutions for a wide range of industrial heat exchangers, supporting operational efficiency and compliance.
Tip: Always verify that the selected welded phe meets regulatory compliance for your specific process.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Many engineers encounter pitfalls during welded phe selection. Material selection often causes problems when the operational environment is not fully understood. Surface finish matters because a smooth and polished surface prevents deposit accumulation and enhances corrosion resistance. Precision in welding is essential to avoid crevices and defects that can lead to corrosion. Quality control ensures material integrity and compliance with regulatory standards. The table below highlights common pitfalls and solutions:
Common Pitfalls | Solutions |
|---|---|
Material selection | Assess fluid types and potential corrosive elements. |
Surface finish | Use polished surfaces to resist deposits and corrosion. |
Precision in welding | Apply accurate welding techniques to prevent defects. |
Quality control | Conduct thorough inspections and follow industry standards for compliance. |
Optimizing flow rates also prevents stagnation, reducing localized corrosion risks and improving performance.
Welded PHE Decision Checklist
A decision checklist helps engineers ensure compliance and maximize performance in industrial heat exchangers. Key items include:
Component dimensional checks for precision.
Material verification through documentation.
Weld and joint inspection for integrity.
Surface finish and workmanship quality checks.
Pressure and leak testing during inspections.
The table below summarizes essential issues and immediate actions:
Issue | Description | Immediate Action |
|---|---|---|
Corrosion | Material degradation from chemical reactions | Use corrosion-resistant coatings and materials |
Fouling and Scaling | Accumulation reduces efficiency and raises energy use | Apply mechanical and chemical cleaning methods |
Tube Leaks and Cracks | Fatigue or defects cause fluid cross-contamination | Consider tube plugging or replacement |
Engineers should confirm regulatory compliance at every stage. Regular maintenance and inspections support long-term efficiency and energy efficiency. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from heattransfer provides solutions that meet strict compliance standards and deliver reliable performance for industrial applications.
Selecting a welded plate heat exchanger for industrial use involves several steps:
Determine the purpose for heating or cooling.
Assess operating conditions and pressure.
Evaluate fluid properties.
Consider pressure drop.
Choose materials for corrosion resistance.
Review maintenance needs.
Check installation space.
Analyze initial and operating cost.
Ensure compliance with industry standards.
Confirm ongoing compliance through inspections.
The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from heattransfer offers proven reliability and compliance. The table below highlights features that support long-term performance and compliance in industrial settings:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Leak-proof operation | Welded plate pack prevents leaks, supporting compliance in high-pressure use. |
High-pressure capability | Handles extreme conditions, meeting compliance for demanding applications. |
Superior heat transfer | Fishbone plates deliver strong performance and compliance with thermal needs. |
Versatile applications | Suitable for many media, ensuring compliance across industries. |
Quality manufacturing | Automated welding meets compliance with global standards. |
Companies should use the checklist and consult Shanghai Heat Transfer for tailored solutions. Advanced heat exchanger solutions deliver reliable performance, lower cost, and help maintain compliance throughout the product lifecycle.
FAQ
What industries use welded plate heat exchangers?
Many industries use welded plate heat exchangers. These include oil and gas, chemical processing, food and beverage, power generation, and marine sectors. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from heattransfer fits a wide range of industrial applications.
How does a welded PHE differ from a gasketed PHE?
A welded PHE uses welded plates to create strong, leak-resistant channels. Gasketed PHEs use gaskets between plates. Welded models handle higher pressures and temperatures. They also work better with aggressive or hazardous fluids.
What materials are available for the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger?
heattransfer offers the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger in stainless steel, titanium, and Hastelloy. These materials provide excellent corrosion resistance and durability. The right choice depends on the fluids and process conditions.
How often should a welded plate heat exchanger be cleaned?
Cleaning frequency depends on the process and the type of fluids. Many users clean their welded plate heat exchangers every few months. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger supports cleaning-in-place systems for easy maintenance.
Can the TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger handle extreme temperatures?
Yes. The TP Welded Plate Heat Exchanger from heattransfer operates from -196°C to 900°C. It also withstands pressures up to 60 bar. This makes it suitable for demanding industrial environments.





